2013 in science
| 2013 in science |
|---|
| Fields |
| Technology |
| Social sciences |
|
| Paleontology |
| Extraterrestrial environment |
| Terrestrial environment |
| Other/related |

A number of significant scientific events occurred in 2013, including the discovery of numerous Earthlike exoplanets, the development of viable lab-grown ears, teeth, livers and blood vessels, and the atmospheric entry of the most destructive meteor since 1908. The year also saw successful new treatments for diseases such as HIV, Usher syndrome and leukodystrophy, and a major expansion in the use and capabilities of technologies such as 3D printing and autonomous cars.
The United Nations designated 2013 the International Year of Water Cooperation.
Events, discoveries and inventions
January

- 2 January
- A study by Caltech astronomers reports that the Milky Way Galaxy contains at least one planet per star, resulting in approximately 100–400 billion exoplanets. The study, based on planets orbiting the star Kepler-32, suggests that planetary systems may be the norm around stars in our galaxy.
- Astronomers report the discovery of giant "geysers" of charged particles emanating from the core of the Milky Way Galaxy. These outflows, which extend as far as 50,000 light-years from the galactic plane, are thought to be fuelled by intense star formation.
- LG Electronics releases the first commercial OLED television. OLED screens are thinner, more efficient and capable of displaying images with greater definition than conventional LCD and plasma screens.
- 3 January
- Physicists create a potassium-based quantum gas which can be manipulated by lasers and magnetic fields to reach negative temperatures. At such temperatures, matter begins to exhibit previously unknown qualities.
- Scientists analyse a meteorite, NWA 7034, that was found in the Sahara Desert and purchased in Morocco in 2011, and report that it is a new type of Mars rock with an unusually high water content.
- American researchers state that a gene associated with active personality traits is also linked to increased longevity.
- 4 January
- Britain's first hand transplantation operation is successfully conducted.
- Toyota demonstrates an autonomous car capable of sensing and reacting to its surroundings, monitoring its driver and communicating with other vehicles.
- 6 January
- British researchers successfully cure blindness in mice using an injection of photosensitive cells. Following additional testing, the treatment could be used to heal humans with retinitis pigmentosa.
- China is reported to be experiencing a rapid growth in the use of industrial robots, with robot installations increasing at over 10 percent a year.

- 7 January
- Australia experiences its hottest day on record, with nationwide average temperatures exceeding 40°C amid one of the most intense bushfire seasons in the country's history.
- Remarkably well-preserved zinc pills are discovered aboard a 2,000-year-old Roman shipwreck, giving a rare insight into Roman medicine.
- Astronomers at the Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (CfA) report that "at least 17 billion" Earth-sized exoplanets are estimated to reside in the Milky Way Galaxy.
- 8 January
- The 2013 Consumer Electronics Show opens in Las Vegas, Nevada. Among the new technologies showcased are flexible tablet computers, autonomous cars, medical telepresence robots, ultra-definition TVs and high-efficiency microchips.
- The German defence company Rheinmetall successfully demonstrates a high-powered military laser that can destroy drones in mid-flight and cut through steel from over 1 mile (1.6 km) away, even in adverse weather conditions. The company plans to mount the laser on a variety of vehicles for battlefield use.
- American astronomers announce the discovery of seven new exocomets – more than double the previously known number of such objects. The exocomets were discovered using the McDonald Observatory in Texas, which imaged the chemical signatures of the comets' tails.
- Astronomers affiliated with the Kepler space observatory announce the discovery of KOI-172.02, an Earth-like exoplanet candidate which orbits a star similar to the Sun in the habitable zone, and is possibly a "prime candidate to host alien life".
- 9 January
- A gamma secretase inhibitor previously experimented for treating Alzheimer's disease is found to have regenerative effects on inner ear hair cells, potentially allowing for the effective treatment of deafness.
- The most distant known supernova is discovered by the Hubble Space Telescope, at a distance of around 10 billion light-years.
- Medical researchers state that sickle cells can be induced to attack treatment-resistant tumours by starving them of blood.
- British and Canadian researchers create a tablet computer which is as thin as paper and also flexible.
- 10 January
- Half of all food is wasted worldwide, according to a new report by the British Institution of Mechanical Engineers (IME).
- The English general lighthouse authority activate a new backup navigation system that allows ships to navigate even if their GPS signals fail.
- The first vessel of a new class of nuclear submarine goes into service with the Russian Navy, featuring a built-in escape pod to allow crew members to survive a critical hull breach.
- An American company unveils a smart hunting rifle which uses a computerised scope, onboard aiming software and laser rangefinders to ensure great accuracy even in the hands of novice shooters. The rifle is also Wi-Fi-enabled, and its software can record its aiming and firing history, potentially allowing law enforcement agencies to track its use.
- 11 January
- Manchester University chemists develop a functional molecular machine, only a few nanometers in size, that can assemble complex molecular structures in a fashion similar to DNA ribosomes. The invention could be used to precisely fashion new medicines or polymers.
- Astronomers discover a distant cluster of supermassive quasars that is both the largest and brightest structure in the known universe, spanning approximately four billion light-years.
- New high-precision observations of the asteroid 99942 Apophis reveal that it is almost certain that the asteroid will not strike the Earth in 2036, despite earlier scientific concern over its trajectory.
- Scientists develop a Breathalyzer-like breath test that could be used to quickly and accurately diagnose lung infections.
- 12 January – Official sources state that Beijing's air is now hazardous to human health, after years of mounting air pollution. The city's air contains as much as 20 times the World Health Organization's recommended amount of toxic particles.
- 13 January – Massachusetts doctors invent a pill-sized medical scanner that can be safely swallowed by patients, allowing the esophagus to be more easily scanned for diseases.
- 15 January – The first museum of 3D-printed artifacts opens in China.
- 17 January – NASA announces that the Kepler space observatory has developed a reaction wheel issue and will discontinue operation for 10 days in the interest of solving the problem. Three functional reaction wheels are needed to accurately aim the telescope; one of Kepler's original four reaction wheels failed in July 2012. If this second wheel issue is not resolved, NASA may be forced to end the long-running Kepler mission altogether.
- 18 January – Japanese researchers create a "privacy visor" which uses near-infrared light to render its wearer unrecognizable to facial recognition software.
- 20 January – Scientists prove that quadruple-helix DNA is present in human cells.
- 21 January – Architects begin preparations for constructing the world's first 3D-printed building. The building will be constructed of a high-strength artificial marble laid down by an industrial-scale 3D printer, and is planned for completion in 2014.
- 22 January
- French glaciologists release a report stating that the glaciers of the Andes are melting at an unprecedented rate.
- NEC and Corning Inc. develop a multi-core fiber optic cable that can transfer a record-breaking petabit of data per second.
- The private spaceflight venture Deep Space Industries announces plans to begin scanning and mining asteroids for precious metals. The company intends to launch its first prospecting spacecraft in 2015.
- A resolution is introduced to the United States Congress to designate 12 February 2013 (Charles Darwin's 204th birthday) as "Darwin Day" in order to recognize "the importance of sciences in the betterment of humanity".

- 23 January
- Scientists encode large amounts of digital information, including the complete sonnets of William Shakespeare, on a single strand of synthetic DNA. DNA has immense potential as a storage medium, and may become commercially available for this purpose in the near future.
- Scientists resume controversial research into the H5N1 influenza subtype, which was previously halted due to fears of biological terrorism.
- A British amputee becomes the first person in the UK to receive the Michelangelo Hand, an advanced new bionic hand, which uses electrodes to precisely mimic muscle movements and which can be used even for delicate engineering tasks.
- Kenya begins the construction of the Konza Technology City, a planned city that is hoped to become a hub of African science and technology upon its completion in 2030.
- 24 January – Britain's Chief Medical Officer warns that antibiotic resistance could have "apocalyptic" consequences, with numerous common bacterial infections becoming increasingly resistant to treatment.
- 25 January
- An international team of scientists develops a functional light-based "tractor beam", which allows individual cells to be selected and moved at will. The invention could have broad applications in medicine and microbiology.
- Scientists design an evolution-inspired organic solar cell with a novel geometric pattern that increases its energy-harvesting efficiency.
- New measurements performed by European scientists reveal that the radius of the proton is 4 percent smaller than previously estimated.
- 27 January – Asteroid 274301, a main belt asteroid, is officially renamed "Wikipedia" by the Committee for Small Body Nomenclature.
- 28 January
- Bolivian scientists restore brain function to stroke-affected rats by injecting them with stem cells. This breakthrough may lead to more effective treatments for strokes in humans.
- American medical researchers develop a painless polymer skin patch that can be used to inject DNA vaccines without a conventional needle, and also increases the initial effectiveness of the vaccine delivered.
- An American research team uses the world's most powerful supercomputer at the time – the IBM Sequoia – to perform a record-breaking computation, modelling an experimental jet engine on over one million processor cores.
- Iran successfully launches a live rhesus monkey into space and recovers the animal safely, in what is claimed to be a prelude to the country's future human spaceflight efforts.
- American scientists finish drilling down to the subglacial Lake Whillans, which is buried around 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) under the Antarctic ice.

- 29 January
- NASA reports that the Kepler space observatory has successfully returned to "science data collection" mode, after suffering a reaction wheel malfunction earlier in the month.
- ESA scientists report that the ionosphere of the planet Venus streams outwards in a manner similar to "the ion tail seen streaming from a comet under similar conditions."
- 30 January – South Korea conducts its first successful orbital launch, using the Naro-1 rocket to place a satellite into orbit.
- 31 January
- British scientists achieve a breakthrough in synthetic biology, developing microscopic biological "factories" that can be assembled in hours and which could be used to deliver medicines, produce biofuels and mine underground minerals.
- Scientists sequence the genome of the domestic pigeon, discovering that all modern pigeon breeds are descended from the wild rock dove.
- The ESA, in collaboration with a group of architectural firms, designs and tests a 3D-printed structure that can be built out of lunar regolith to serve as a Moon base.
- Japanese scientists genetically modify a transparent zebrafish specimen to produce a visible glow during periods of intense brain activity, allowing the fish's "thoughts" to be recorded as specific regions of its brain light up in response to external stimuli.
February
- 1 February
- Stanford University physicists discover that atom-thin sheets of graphene are 100 times more chemically reactive than thicker sheets. This reactivity may be crucial to developing new practical applications for graphene, which is already widely known for its immense strength and conductivity.
- Medical researchers develop a new method of efficiently detecting cancer using bioelectric signals. In addition, they were able to manipulate cellular electric charge levels to prevent certain cells from developing cancer.
- 2 February
- Iran unveils the Qaher-313 which it claims is its first stealth fighter.
- Californian researchers use genetic modification to rejuvenate ageing blood cells, strengthening the immune systems of elderly mice. If human trials prove successful, this treatment could allow older people to more effectively resist disease.
- 3 February
- The Scottish Government announces plans for a national physics prize named in honour of Peter Higgs, who first theorized the Higgs boson in 1964.
- The British Army begins using a miniature drone helicopter in Afghanistan. The aerial surveillance robot weighs just 16 grams, and can be remotely piloted into difficult terrain to detect hidden enemy positions.

- 4 February
- American researchers develop a new molecular therapy which can cross the blood–brain barrier to deliver medicines to the brain, potentially helping to treat neurological diseases such as Parkinson's disease.
- A much-vaunted experimental vaccine for tuberculosis proves to be largely ineffective against the disease in human trials.
- After DNA testing, scientists confirm that a medieval skeleton unearthed in Leicester is that of the defeated Plantagenet king Richard III, who was killed in battle in 1485.
- Australian engineers build a "quantum microscope" which offers unprecedented levels of precision in measuring live biological systems.
- Sea urchins are discovered to be capable of efficiently converting carbon dioxide into raw material for their shells, potentially offering a new method of carbon capture for industrial purposes.
- 5 February
- Scientists at Scotland's Heriot-Watt University develop a 3D printer that can produce clusters of living stem cells, potentially allowing complete organs to be printed on demand in future.
- American researchers partially cure Usher syndrome in mice, a severe form of congenital deafness, using a precisely targeted gene therapy.
- 6 February
- Halley VI, a new British Antarctic research station, begins operation. The station, which is mounted on hydraulic ski-legs to allow it to be towed across the ice, features an advanced modular design and is expected to endure the Antarctic climate until 2050.
- In a series of separate developments, American and Japanese engineers create 3D printers that can produce edible meals with a range of flavours and textures on demand. These could both replace conventional ready meals and allow astronauts to enjoy a far more varied diet.
- Astronomers report that 6% of all dwarf stars – the most common stars in the known universe – may host Earthlike planets. Additionally, some such exoplanets may exist only 13 light-years from Earth.
- Scientists discover live bacteria in the subglacial Antarctic Lake Whillans.
- 8 February
- Scientists use an extensive genetic and phenotypic database to determine the common ancestor of all modern placental mammals, including humans.
- New York researchers successfully cure leukodystrophy in mice by using skin cells to repair damaged myelin sheaths. This treatment may also prove effective in curing human multiple sclerosis.
- 10 February
- NASA's Curiosity Mars rover uses its onboard drill to obtain the first deep rock sample ever retrieved from the surface of another planet.
- A genetically engineered strain of the vaccinia virus is found to triple the average survival time of patients with a severe form of liver cancer.
- 12 February – North Korea conducts its third nuclear test despite international sanctions and condemnation.
- 13 February
- The ESA's CryoSat detects a significant decline in Arctic ice cover.
- Scientists successfully cure type 1 diabetes in dogs using a pioneering gene therapy.

- 14 February
- University of Oxford engineers construct an autonomous car that can be easily switched between manual and self-driving modes.
- The Large Hadron Collider (LHC) begins a planned two-year shutdown, during which it will undergo a major systems upgrade. Upon its reactivation in 2014, the LHC will operate at an energy of approximately 14 teraelectronvolts – double its current maximum energy.
- Researchers develop a specialized neural implant which gives rats the ability to sense infrared light – a pioneering use of implant technology to grant living creatures new abilities, instead of simply replacing or augmenting existing ones.
- The United States Food and Drug Administration approves the first functional commercial bionic eye, the Argus II, for the treatment of blindness. The device, which became available in Europe in 2011, uses a combination of ocular implants and camera-equipped glasses to restore vision to people blinded by retinitis pigmentosa.
- 15 February
- A 10-ton meteoroid impacts in Chelyabinsk, Russia, producing a powerful shockwave and injuring over 1,000 people.
- The asteroid 2012 DA14, which masses around 130,000 tons, makes the closest Earth flyby yet recorded for a large asteroid, passing within 27,000 kilometres (17,000 mi) of the Earth's surface.
- 18 February – Studies of a recently discovered Higgs boson-like particle suggest that the universe may end in a false vacuum collapse billions of years from now.
- 19 February
- The UK government pledges to provide advanced bionic limbs for all British soldiers who have lost limbs in combat.
- A new species of bent-toed gecko is formally described, having been discovered in Vietnam.
- 20 February
- NASA reports the discovery of Kepler-37b, the smallest exoplanet yet known, around the size of Earth's Moon.
- Internet entrepreneurs Sergey Brin and Mark Zuckerberg announce a new global prize for excellence in the life sciences, offering US$3 million to each recipient.
- The President of the United States, Barack Obama, announces the Brain Activity Map Project – a decade-long collaborative effort to map the structures and functions of the human brain, with the aim of yielding new treatments for a range of neural diseases.
- 21 February
- Cornell University scientists use a 3D printer to create a living artificial ear from collagen and ear cell cultures. In future, such ears could be grown to order for patients with ear trauma or amputation.
- The deepest known hydrothermal vents are discovered in the Caribbean at a depth of almost 5,000 metres (16,000 ft).
- A study finds that bumblebees can sense electric fields around flowers.
- University of Pennsylvania researchers develop a "protein passport" able to bypass the body's immune system. This could aid the delivery of medicinal nanoparticles in future nanomedicine.
- 22 February – Data gathered from Siberian ice caves reveals that continued global warming may lead to widespread thawing of permafrost, potentially releasing massive volumes of trapped carbon dioxide and methane into the atmosphere.

- 23 February – A US inventor builds a "spider-sense" bodysuit, equipped with ultrasonic sensors and haptic feedback systems, which can alert its wearer of approaching threats and allow them to detect and respond to attackers even when blindfolded.
- 24 February
- Oxford University researchers discover the mechanism by which certain brain cells are able to survive being starved of oxygen. In future, this research may yield more effective stroke treatments.
- A study finds that chimpanzees solve puzzles for entertainment just as humans do.
- Scientists announce that they have found fragments of Rodinia, an ancient "lost" supercontinent, in what is now the Indian Ocean.
- 25 February
- Israel successfully tests its Arrow 3 missile defence system, designed to destroy enemy ballistic missiles while they are still high in the Earth's atmosphere.
- 26 February
- American engineers develop a wirelessly charged flexible battery that can continue to function even if stretched to three times its usual size. With further development, the invention could be used to power flexible smartphones, tablets and medical electronics.
- A study finds that sleep loss can alter the behavior of genes, which may explain why it often precedes more serious medical problems such as diabetes, obesity, and heart disease.
- 27 February
- Astronomers use the NuSTAR satellite to accurately measure the spin of a supermassive black hole for the first time, reporting that its surface is spinning at almost the speed of light.
- An American company constructs a lightweight, high-efficiency urban car with an entirely 3D-printed plastic body that is as damage-resistant as steel. The vehicle's construction is entirely automated, requiring no human input beyond the uploading of the car's design.
- 28 February
- Duke University researchers successfully connect the brains of two rats with electronic interfaces that allow them to directly share information, in the first-ever direct brain-to-brain interface.
- A study finds common genetic links between five major psychiatric disorders: autism, ADHD, bipolar disorder, depression, and schizophrenia.
- Astronomers make the first direct observation of a protoplanet forming in a disk of gas and dust around a distant star.
- A third radiation belt is discovered around the Earth.
- Researchers identify adult stem cells in the bone marrow that could one day be used to treat inflammatory bowel disease (IBD).
March

- 1 March – Boston Dynamics demonstrates an updated version of its BigDog military robot, a mule-sized heavy-lifting robot able to navigate rough terrain and equipped with an arm powerful enough to easily lift and throw breeze blocks.
- 3 March – American scientists report that they have cured HIV in an infant by giving the child a course of antiretroviral drugs very early in its life. The previously HIV-positive child has reportedly exhibited no HIV symptoms since its treatment, despite having no further medication for a year.
- 4 March
- Scientists announce that they have directly measured the polarization of light, overcoming aspects of the uncertainty principle.
- DARPA begins efforts to develop a fleet of small naval vessels capable of launching and retrieving combat drones without the need for large and expensive aircraft carriers.
- In a U.S. first, researchers replace a large part of an injured patient's skull with a precision 3D-printed polymer replacement implant.
- 5 March – The Human Connectome Project releases the most detailed scans of the human brain yet made, allowing neuroscientists to more accurately study the complexities of the brain's structure and identify the causes of neural disorders.
- 6 March
- After studying the DNA of a modern African American, scientists estimate that the Y-chromosomal Adam – the most recent male common ancestor of human beings – lived much earlier than previously thought, over 338,000 years ago.
- Chinese and Israeli scientists develop a Breathalyzer-style breath test that can quickly and easily diagnose stomach cancer by analyzing exhaled chemicals, without the need for an intrusive endoscopy.
- 7 March
- After an eight-year project involving the use of a pioneering cloning technique, Japanese researchers create 25 generations of healthy cloned mice with normal lifespans, demonstrating that clones are not intrinsically shorter-lived than naturally born animals.
- An international project known as Bedmap2 analyses 50 years of data to measure the volume of Antarctic ice, finding it to be 26,500,000 cubic kilometres (6,400,000 cu mi), which would raise global sea levels by 58 metres (190 ft) if it melted.
- Scientists from Oregon State University reconstruct the global temperature record since the end of the last ice age. Their data, taken from 73 sites around the world, shows a clear and rapid warming trend in the 20th and early 21st centuries.
- Tests on mice demonstrate conclusive proof that resveratrol, a compound found in red wine, improves health and longevity.
- 9 March
- British dental researchers grow viable teeth from a combination of gingival cells and stem cells, potentially allowing future patients to receive living teeth to replace diseased or damaged ones.
- Roboticists launch an online database and cloud computing platform which can be accessed by robots worldwide, allowing them to more easily recognise unfamiliar objects and perform intensive computing tasks.
- 11 March
- Astronomers discover the binary brown dwarf Luhman 16 (WISE 1049–5319) at a distance of 6.5 light years from Earth – the closest star system to be discovered since 1916.
- A study concludes that heart disease was common among ancient mummies.
- Researchers develop smart self-healing circuits that can rapidly restore themselves to a fully functional state by detecting and neutralising electronic faults.

- 12 March
- NASA's Curiosity rover finds evidence that conditions on Mars were once suitable for microbial life after analyzing the first drilled sample of Martian rock, "John Klein" rock at Yellowknife Bay in Gale Crater. The rover detected water, carbon dioxide, oxygen, sulfur dioxide, hydrogen sulfide, chloromethane and dichloromethane. Related tests found results consistent with the presence of smectite clay minerals.
- Japan becomes the first country to successfully extract natural gas from offshore methane clathrate deposits.
- 13 March
- The Atacama Large Millimeter Array, at the time the world's most powerful radio telescope, becomes fully operational in northern Chile.
- Lockheed Martin develops a new method for desalination that is reportedly vastly cheaper and more efficient than conventional methods. The new technique uses carbon membranes with nanoscale pores to efficiently filter salt molecules from seawater to make drinkable water.
- 14 March
- CERN scientists confirm, with a very high degree of certainty, that a new particle identified by the Large Hadron Collider in July 2012 is the long-sought Higgs boson.
- Scientists induce monkey skin cells to become healthy brain cells which function normally when implanted into the donor monkey's brain. This breakthrough suggests that such personalized medicine approaches could be effective in human patients.
- 15 March – Scientists working on the Lazarus Project announce that they have successfully rejuvenated cells of Rheobatrachus silus, a species of frog extinct since 1983.
- 16 March – Japanese researchers unveil the "smelling screen", a digital display screen capable of emitting pinpointed smells.
- 17 March
- New data suggests that the Mariana Trench, the deepest point on the Earth's surface, is home to a large amount of bacterial life forms. Other researchers reported related studies that microbes thrive inside rocks up to 580 m (1,900 ft) below the sea floor under 2,600 m (8,500 ft) of ocean off the coast of the northwestern United States.
- Shams 1, the world's largest concentrated solar power plant, becomes operational in Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates.
- 18 March
- If global average temperatures rise by just 2 °C, the number of extreme storm surges like Hurricane Katrina will increase tenfold, according to new research.
- US scientists successfully map 80% of the neurons in a vertebrate brain at cellular-level resolution in just 1.3 seconds.
- NASA reports evidence from the Curiosity rover on Mars of mineral hydration, likely hydrated calcium sulfate, in several rock samples, including the broken fragments of "Tintina" rock and "Sutton Inlier" rock as well as in the veins and nodules in other rocks like "Knorr" rock and "Wernecke" rock. Analysis using the rover's DAN instrument provided evidence of subsurface water, amounting to as much as 4% water content, down to a depth of 60 cm (2.0 ft).
- Pluto may have up to 10 moons, along with at least one ring system, according to a new study.
- 19 March

- The Neanderthal genome is sequenced by German scientists from a toe bone found in southern Siberia.
- Scientists announce they can now illuminate up to 100 biomarkers, ten times more than the previous standard. This breakthrough may make it much easier to spot proteins in cancer cells – a vital diagnostic technique.
- NASA reports that a software computer problem on the Curiosity Mars rover is now repaired.
- Researchers at the University of Cambridge demonstrate a virtual "talking head" with realistic emotions, which could lead to more naturalistic human-computer interactions.
- Swiss scientists develop a medical scanner that can be implanted just under the skin and can monitor a range of blood-related conditions, providing instant results via mobile phone. They say it will be available to patients by 2017.
- 20 March – Gene therapy is used to cure leukaemia in three adult patients.
- 21 March
- The European-led research team behind the Planck cosmology probe releases the mission's all-sky map of the cosmic microwave background. The map suggests the universe is slightly older than thought; according to the team, the universe is 13.798 ± 0.037 billion years old, and contains 4.9% ordinary matter, 26.8% dark matter and 68.3% dark energy. Also, the Hubble constant was measured to be 67.80 ± 0.77 (km/s)/Mpc.
- Scientists develop a video screen that allows users to see 3D images without using special glasses.
- Scientists develop genetically engineered T-lymphocytes that have been proven successful in treating cases of acute lymphoblastic leukaemia.
- 22 March – At the 44th annual Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, scientists announce the discovery of the first known meteorite to originate from Mercury. The green rock, known as NWA 7325, is thought to be 4.56 billion years old.
- 24 March
- Supplementation of the protein SNX27 reverses the Down syndrome phenotype in mice, according to new research.
- Scientists discover mutations in 26 genes that are believed to be responsible for oesophageal cancer, a breakthrough that could lead to new drug treatments for the disease.
- 27 March – A potential new weight loss method is discovered, after a 20% weight reduction was achieved in mice simply by having their gut microbes altered.
- 28 March
- New research suggests that the cloth in the Turin Shroud, rather than being medieval in origin, likely dates from between 300 BC and 400 AD.
- Stanford researchers announce the construction of a working transistor-like device, dubbed a transcriptor, out of DNA and RNA molecules.
- 29 March – Scientists create a robotic ant colony that behaves like a real one. The tiny machines can be programmed to avoid obstacles and find the quickest route through a network or maze.
April

- 3 April
- A breakthrough is achieved in the production of hydrogen fuel, allowing large quantities to be extracted from any plant.
- A new study suggests that common cholesterol-reducing drugs may also prevent macular degeneration.
- NASA scientists report that hints of dark matter may have been detected by the Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer on the International Space Station. According to the scientists, "the first results from the space-borne Alpha Magnetic Spectrometer confirm an unexplained excess of high-energy positrons in Earth-bound cosmic rays."
- NASA states that complex organic chemicals could arise on Titan, a moon of Saturn, based on studies simulating the atmosphere of Titan.
- 4 April
- The discovery of the most distant supernova yet found is announced.
- Scientists construct a 3D printer which can create material very similar to human tissue.
- A new species of giant tarantula, Poecilotheria rajaei, is formally described, having been discovered in Sri Lanka in 2009.
- American scientists announce that they have identified a number of genetic markers that are associated with an increased risk of Alzheimer's disease.
- A new camera system is developed that can generate high-resolution 3D images from up to a kilometre away.
- 7 April – A US startup company develops plant-derived proteins that can be used as a sustainable, environmentally friendly substitute for eggs in almost all food products.
- 9 April
- At the 2013 Sea-Air-Space Exposition, American defense companies display prototypes of numerous advanced weapons technologies, including viable railguns, VTOL airships and grenade-sized reconnaissance robots.
- British researchers discover that a mutation of the gene BRCA2 increases both the risk and severity of prostate cancer in men, as well as being linked to hereditary breast cancer in women.
- Chinese scientists develop a carbon-based aerogel which they claim is the lightest material yet produced, with a density only slightly greater than that of air.
- Scientists state that climate change may cause a significant increase in air turbulence over the North Atlantic by 2050, potentially endangering passenger aircraft.
- 10 April
- Stanford University researchers develop "CLARITY", a method of making brain tissue transparent using acrylamide, allowing brain structures to be studied in unprecedented detail without requiring extensive biopsies.
- Scientists develop the first objective method of measuring pain by directly studying the brains of patients.
- Scientists find that, by inhibiting the SEC24A gene, cholesterol levels in mice can be reduced by 45%, offering hope for an alternative or complementary therapy to statins.
- 11 April
- International researchers discover key similarities in the brains of arthropods and vertebrates, potentially aiding scientific understanding of the causes of human neural diseases.
- Philips demonstrates a new type of LED lighting that is reportedly twice as energy-efficient as any previous electric lightbulb.
- A study finds that carefully timed sounds played during sleep can enhance memory.
- NASA reports the possible finding of the "debris field" of the 1971 Soviet Mars 3 lander on the planet Mars. Images taken by the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter seem to show the possible remains of the parachute, retrorockets, heat shield and lander.
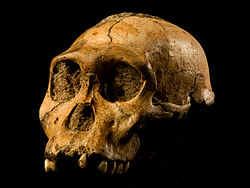
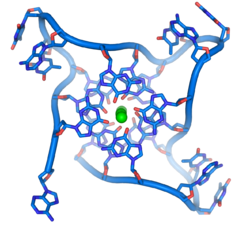
- 12 April
- Animal trials are set to begin on a gene therapy for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis – a degenerative condition that Stephen Hawking has.
- Scientists reconstruct the skeleton of the ancient hominid Australopithecus sediba, discovering that it possessed a unique mixture of human- and ape-like traits.
- The first building to be entirely powered by algae is constructed in Hamburg.
- 15 April
- A functional lab-grown kidney is successfully transplanted into a live rat in Massachusetts General Hospital. This breakthrough is a major step forward for the nascent field of regenerative medicine.
- The Cryogenic Dark Matter Search experiment reports the possible discovery of traces of dark matter, although further experimental confirmation is required.
- 16 April – American medical researchers develop a new type of bandage which uses microscopic needles to adhere to injured flesh. The bandage requires no adhesive chemicals, is significantly stronger than existing medical adhesives, and could offer a safer and more efficient means of securing skin grafts.
- 17 April
- Scientists develop a new form of lithium-ion battery which is thousands of times more powerful than current battery technologies, while also charging much faster. The battery utilises a compact 3D design, intertwining its electrodes to maximize its surface area while reducing its volume.
- MIT researchers determine the structure of bones down to the molecular level, using supercomputer simulations twinned with studies of real bone fibers. Their data grants new insights into the compounds that grant living bone its strength, and may permit the manufacture of versatile new biomimetic materials.
- The genome of the coelacanth, an endangered deep-sea "living fossil", is sequenced.
- 18 April – NASA announces the discovery of three new Earthlike exoplanets – Kepler-62e, Kepler-62f, and Kepler-69c – in the habitable zones of their respective host stars, Kepler-62 and Kepler-69. The new exoplanets, which are considered prime candidates for possessing liquid water and thus potentially life, were identified using the Kepler spacecraft.
- 21 April
- The Antares rocket, a commercial launch vehicle developed by Orbital Sciences Corporation, successfully conducts its maiden flight.
- A study concludes that stress leads to faster growth in squirrels.

- 22 April
- Biologists use antibodies to transform bone marrow stem cells directly into healthy brain cells. This breakthrough may allow neurological injuries and illnesses to be more effectively treated, and reduces the risk of immune rejection.
- University of Exeter scientists report the creation of a genetically modified strain of E. coli bacteria which can convert sugar into diesel fuel.
- A British engineer unveils a giant "mantis" robot, large enough to carry a human pilot, which is supported by multiple hydraulic legs. The robot has reportedly attracted the interest of mining and marine research companies.
- 24 April
- IBM develops a robot which combines telepresence and augmented reality technologies to assist engineers working on complex projects in remote areas.
- CERN releases new particle-collision data from the Large Hadron Collider which may help explain why matter became dominant over antimatter in the early universe.
- 25 April – A partial lunar eclipse occurs.
- 26 April
- Following laboratory tests of molten iron, European scientists determine that the Earth's core has a temperature of 6,000 degrees Celsius, 1,000 degrees hotter than previously thought. This discovery may help explain why the planet has such a strong geomagnetic field.
- US and Chinese scientists develop a sensor array which is as sensitive to touch and pressure as the human fingertip. The invention may pave the way for new robotic sensors, electronic interfaces and types of artificial skin.
- 27 April – Design approval is given for a crucial reactor component of the ITER nuclear fusion project, which is currently under construction in Cadarache, France, and is expected to begin generating fusion power in 2022.
- 29 April
- After years of unpowered glide tests, Scaled Composites' SpaceShipTwo hybrid spaceplane successfully conducts its first rocket-powered flight.
- The ESA's Herschel Space Observatory runs out of liquid helium coolant, marking the end of its highly productive four-year mission to observe the far infrared universe.
- NASA's Cassini spacecraft photographs an enormous hurricane on Saturn, more than 20 times the size of the average terrestrial hurricane.
- NASA-funded scientists in Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute claim that, during experiments on the International Space Station, microbes seem to adapt to the space environment in ways "not observed on Earth" and in ways that "can lead to increases in growth and virulence".
May
- 1 May
- IBM scientists release A Boy and His Atom, the smallest stop-motion animation ever created, made by manipulating individual carbon monoxide molecules with a scanning tunnelling microscope.
- Researchers discover that boron nitride – a nanomaterial also known as "white graphene" – is highly effective at removing harmful chemicals from polluted water, and could be used to clean up future oil spills.
- American engineers create a multi-lens digital camera that mimics an insect's compound eye, providing immense depth of field without distorting the image.
- 2 May – Harvard scientists unveil RoboBee, a miniature robot with the smallest ever man-made wings capable of flight.
- 3 May
- Scientists announce the discovery of a previously unknown meat-eating theropod dinosaur, Aorun zhaoi, dating from approximately 161 million years ago. It is the oldest coelurosaur yet discovered.
- Researchers cure epilepsy in mice using transplanted brain cells.

- 6 May
- It is shown that boosting a single gene can increase the maximum lifespan of fruit flies by over 25 percent.
- European researchers announce a potential cure for grey hair.
- American scientists transform skin cells into bone cells using induced pluripotent methods, in which the cells were grown on scaffolding, allowing them to gain a 3D structure. This is the first time a fully functioning three-dimensional bone structure has been created from cell lines.
- A new study finds that children whose parents suck on their pacifiers have fewer allergies later in life.
- Solar engineers discover a method of increasing the efficiency of standard commercial silicon solar cells from 19% to 23%.
- 7 May
- A new study suggests that all Europeans are related to a small group of ancestors dating back only 1,000 years.
- Researchers discover statistical but controversial evidence for the proposed Eurasiatic language superfamily, dating back 15,000 years.
- Scientists identify what may be the earliest known pachycephalosaur, Acrotholus audeti.
- The Alzheimer's drug Gammagard fails to produce results in a large-scale clinical trial.
- 8 May – Researchers achieve a significant breakthrough in understanding genital herpes, which could lead to the development of a vaccine to prevent and treat HSV-2.
- 9 May
- In a breakthrough they describe as "huge", researchers have identified a protein that reduces heart size and thickness in mice. This could potentially offer a way of treating heart failure and aging in humans.
- A congressional hearing Archived 6 December 2014 at the Wayback Machine by two U. S. House of Representatives subcommittees discusses exoplanet discoveries, prompted by the discovery of the exoplanet Kepler-62f, along with Kepler-62e and Kepler-62c. A related special issue of the journal Science, published earlier, described the discovery of the exoplanets.
- 10 May
- An annular solar eclipse occurs.
- The concentration of carbon dioxide (CO2) in Earth's atmosphere reaches a symbolic milestone, passing 400 ppm (parts per million) for the first time in human history.
- Researchers create a form of magnetic graphene that could transform the electronics industry.
- The Royal Canadian Mounted Police report the first known case of a life being saved by a search and rescue drone.
- 11 May – Researchers develop a thermal invisibility device, measuring 5 cm wide, able to "cloak" objects from heat.
- 12 May – It is discovered that Utricularia gibba, a carnivorous bladderwort plant, has the shortest known DNA sequence of any multicellular plant. It largely lacks "junk DNA", sequences of code that do not encode proteins.
- 13 May – Researchers at NYU school of Medicine identify a key protein mutation, called Ras, that is the mechanism through which pancreatic cancer cells acquire nutrients.
- 14 May – Iranian scientists create copper iodide nanostructures by applying pomegranate juice as a reducer.

- 15 May
- Human embryonic stem cells are created by cloning for the first time, with major implications for treating a wide range of diseases.
- NASA reports that a reaction wheel on the Kepler space observatory may be malfunctioning and may result in the premature termination of the observatory's search for Earth-like exoplanets.
- Four genes implicated in "bad" cholesterol have been identified in baboons, a finding that could pave the way for new drugs to prevent human heart disease.
- New fossils provide physical evidence that the evolutionary split between apes and monkeys may have occurred "25 to 30 million years ago", as long suggested by DNA findings.
- New evidence suggests that Mount Everest's glaciers are melting.
- Scientists release pictures of what they believe the lost city of La Ciudad Blanca in La Mosquitia, Honduras.
- A new study finds that the white blood cell levels in men decrease faster during aging than in women, possibly providing one clue as to why women have longer average lifespans.
- Fish have been migrating to the poles for decades, due to climate change, according to a new study.
- A team of Iranian researchers studies nanotechnology applications in neuroscience, reporting new results regarding medicine and drug delivery for the brain and nerves.
- 16 May
- Water dating back 2.6 billion years, by far the oldest ever found, is discovered in a Canadian mine.
- Mild electric shock is shown to provide a lasting improvement to mathematical ability.
- A new world record has been achieved in wireless data transfer, with 40 Gbit/s transferred at 240 GHz over a distance of one kilometer.
- 21 May
- Genetic samples from a museum specimen have revealed the pathogen that caused the 19th-century Great Famine of Ireland. The strain is now thought to be extinct.
- By blocking a protein known as NF-kB that is secreted by the hypothalamus, researchers extend the lifespan of laboratory mice by 20 percent.
- 22 May
- Plans are approved for the world's biggest wave farm in north-west Scotland, with an intended power-generation capacity of 40MW.
- In a significant move to address climate change, China announces that it will impose a cap on carbon emissions by 2016.
- Researchers at Purdue University in West Lafayette, Indiana, report that Earth is pushing the Moon away more quickly than it has done for most of the past 50 million years.
- Researchers in France confirm that atypical activation of different genes distinct to other tissues occur in all kinds of cancer. Tumor cells in lung cancer, for example, express genes, which should be silent, particular to male sperm production. According to the researchers, "The methodical recognition of ectopic gene activations in cancer cells could serve as a basis for gene signature–guided tumor stratification".
- 23 May – Very early symptoms of Huntington's disease, such as depression and anxiety, can be prevented in mice by switching off a protein, according to a new study.
- 25 May – A penumbral lunar eclipse occurs.
- 26 May – Using new algorithms, researchers generate accurate images of sub-cellular structures in milliseconds rather than minutes.

- 27 May
- Four-hundred-year-old bryophyte specimens left behind by retreating glaciers in Canada are brought back to life in the laboratory.
- Archaeologists announce the discovery of nearly 5,000 cave paintings, some of which may date back as early as 6,000 BC, near Burgos, Mexico.
- 28 May – The first graphene-based circuits to break the gigahertz barrier are created by researchers in the US and Italy.
- 29 May
- Aurornis xui is described as the most basal species of Avialae, potentially unseating Archaeopteryx as the oldest known bird.
- Soyuz TMA-09M is launched from the Baikonur Cosmodrome, transporting a three-person crew to the International Space Station.
- Russian scientists announce the discovery of mammoth blood and well-preserved muscle tissue from an adult female specimen in Siberia.
- The Wide-field Infrared Survey Explorer (WISE) discovers 28 asteroid families through the Jupiter-Mars chief asteroid belt. It also finds a large number of formerly concealed and unclassified asteroids through infrared snapshots for the first time.
- A team of chemists and physicists from Japan's Yokohama National University produce a material that can be developed into mixed, conductive 3D formations, enabling scientists to create customized brain electrodes.
- For the first time, astronomers observe a spinning neutron star suddenly slowing down.
- Freescale Semiconductor introduces KL02, a millimeter-scale microchip that contains almost all the components of a tiny functioning computer.
- 30 May
- New analysis suggests that turtles evolved a shell 40 million years earlier than previously thought.
- Stanford University researchers unveil a zinc-air battery that is more energy-dense and cheaper than lithium-ion counterparts.
- Researchers create the first-ever high-resolution images of a molecule as it breaks and reforms chemical bonds.
- Biomedical researchers at SCRM in Edinburgh, Scotland, successfully synthesize human blood using stem cells.
- Researchers at Nanyang Technological University invent a graphene-based sensor that is 1,000 times more sensitive to light than traditional CMOS or CCD sensors.
- Within a century, climate change will threaten extinction for 82 percent of California's native fish, according to researchers at UC Davis.
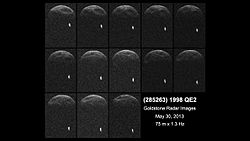
- 31 May
- NASA scientists report a possible human mission to Mars may involve a great radiation risk, based on the amount of energetic particle radiation detected by the RAD on the Mars Science Laboratory while traveling from the Earth to Mars in 2011–2012.
- NASA astronomers report that the near-Earth asteroid 1998 QE2 is passing 3.6 million miles away from the Earth. 1998 QE2 reportedly has its own asteroid moon.
- Researches find fragments of meteorites in pieces of ancient Egyptian jewellery, which were discovered in a cemetery dating back to roughly 3,300 BC near Cairo in 1911.
- Researchers at the University of Birmingham develop an effective hearing aid based on the ear structure of a species of fly, Ormia ochracea.
June
- 1 June – The New York Times reports that "the United States is far and away the world leader in medical spending, even though numerous studies have concluded that Americans do not get better care."
- 4 June
- A new treatment to "reset" the immune system of multiple sclerosis patients is reported to reduce their reactivity to myelin by 50 to 75 percent.
- A newly discovered prehistoric lizard, Barbaturex morrisoni, is named after Doors singer Jim Morrison, who called himself "The Lizard King".
- Microchip maker Intel launches its Haswell series of processors, offering better graphics performance and battery efficiency over the previous processor generation.


- 5 June
- Urban environments have a profound effect on the circadian rhythms of humans and animals, according to a new study.
- Scientists report fossil remains of Archicebus achilles, a primate considered to be the "earliest well-preserved fossil primate ever found," dating back an estimated 55 million years.
- Researchers made a new discovery about tumors in hominids. They report the finding of the first known tumor in the rib of a Neanderthal man who lived more than 120,000 years ago.
- The multi-year global surveillance disclosures are launched and indicate that nearly all major technical possibilities for mass surveillance that emerged in recent decades – such as in Internet infrastructure, software, smartphones and other IC technologies – are proactively exploited or attempted to be exploited by secret services with a public rationale of counter-terrorism.
- 6 June
- For the first time in the United States, a bioengineered blood vessel is transplanted into a patient's arm. The patient, a man with end-stage kidney disease, is part of a clinical trial of laboratory-grown veins.
- Scientists state that most male birds have no penis. They ejaculate sperm out of an exit opening named a cloaca, which is also used for excreting urine and feces.
- Scientists at the IAA-CSIC report the detection of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons in the upper atmosphere of Titan, the largest moon of the planet Saturn.
- 7 June – Breastfeeding boosts brain development compared to formula-fed babies, according to a new study.
- 10 June
- Scientists report that the earlier claims of an Earth-like exoplanet orbiting Alpha Centauri B, a star close to our Solar System, may not be supported by astronomical evidence.
- A new skyscraper elevator is demonstrated using carbon fiber cables to reach heights of 1,000 metres (3,300 ft) or higher in a single trip, without passengers needing to change lifts.
- 11 June
- Scientists at the University of Nottingham discover a previously undetected layer in the human cornea, dubbed Dua's layer.
- The world's first commercially available 5-GHz computer processor is unveiled by AMD.
- 12 June
- A new study suggests that altitude plays a role in language evolution, explaining why ejective sounds are more popular in languages of high-altitude regions.
- Taking the AIDS drug tenofovir greatly reduces the risk of HIV infection among intravenous drug users, according to a new study.
- Scientists discover a method to use pressure to make a material expand instead of compress/contract. The pressure-treated material has half the density of the first state.

- 13 June
- Sleep researchers state that natural sleep allows the brain to combine emotional memory, and also find that a popular sleeping drug heightens the recollection of and response to negative memories.
- Association for Molecular Pathology v. Myriad Genetics, Inc.: The Supreme Court of the United States rules that naturally occurring genes may not be patented, with significant implications for future medical research.
- 14 June
- American researchers identify a key embryonic protein that, though usually deactivated shortly after birth, is reactivated in patients with advanced cancer. This breakthrough may allow for better treatment of advanced cancer cases, which typically respond poorly to currently available therapies. As a result of this discovery, scientists may be able to determine from the structure of the protein the fundamental process through which cancer cells seek out new tumor sites and create secondary tumors after leaving the primary tumor site.
- Scientists combine synchrotron X-rays with scanning tunneling microscopy to create highly detailed images of different materials at the atomic level. By combining the two methods, researchers are now able to not only see where individual atoms reside but also determine a material's chemical and magnetic properties. This discovery could have wide applications in accelerating discoveries in a number of fields, particularly in nanotechnology.
- Sharp Corporation achieves the highest solar cell energy conversion efficiency to date, of approximately 44.4%, using a concentrator triple-junction compound solar cell.
- 17 June
- TOP500 reports that China's Tianhe-2 supercomputer is the world's most powerful computer, capable of performing over 33 quadrillion floating point operations per second.
- Physicists report the possible detection of a new subatomic particle, Zc(3900), a hadron which may be the first tetraquark to have been observed experimentally.
- Two separate teams independently develop prototype flying bicycles. British engineers construct a hybrid bicycle-paraglider capable of flying to an altitude of 4,000 feet (1,200 m), while a Czech team demonstrates a multi-rotor electric "hoverbike" that can hover like a helicopter at low altitudes.
- Engineers demonstrate a small quadrupedal "cheetah-cub" robot, with speed and agility approaching that of a real cat. The prototype is intended as the basis for future search-and-rescue robots with vastly greater speed and agility than human emergency workers.
- Weapons manufacturer MBDA Germany develops a high-powered laser weapon capable of targeting and destroying incoming rockets, artillery shells and UAVs.
- 18 June
- Google launches a fleet of high-altitude balloons capable of beaming wireless internet to remote locations far more cheaply than satellites.
- American scientists use 3D printing to manufacture a new class of microscopic batteries, which may allow the easy production of extremely small medical devices, nanorobots and communications systems.
- British researchers develop high-resolution 3D holograms for the teaching of anatomy to medical students.
- 19 June – Scientists claim that "cancerproof" laboratory animals, such as naked mole-rats, may not get cancer because they produce an "extremely high-molecular-mass hyaluronan", which is over "five times larger" than that in cancer-prone humans and cancer-susceptible laboratory animals.

- 20 June
- Adding silver particles to antibiotics makes them 10 to 1,000 times more effective at fighting infections, research suggests.
- International neuroscientists produce a full-3D map of a human brain, scanning and digitizing thousands of ultrathin slices of the brain to determine its structure at extremely high resolution. The map will be made freely available to medical researchers worldwide.
- During the Shenzhou 10 mission, Chinese astronauts deliver the country's first public video broadcast from the orbiting Tiangong-1 space laboratory.
- The European Intermediate eXperimental Vehicle (IXV), an experimental spacecraft which is intended to make its first orbital launch in 2014, successfully conducts a parachute drop test over the Mediterranean Sea.
- Physicists develop a table-top particle accelerator with 2 gigaelectronvolts (GeV) of power, downsizing a conventional accelerator by a factor of 10,000.
- American engineers create a functional, rechargeable nanoscale battery out of wood. The conductive wooden fibers, coated with tin, are longer-lasting than any previous nanoscale battery.
- The Israeli-based company NeuroDerm reports good trial results for a new Parkinson's disease treatment, which involves dermal introduction of two separate drugs.
- 21 June – Following groundbreaking laboratory tests, researchers discover that plants make use of quantum effects to efficiently channel photons during photosynthesis.
- 23 June
- Scientists find that plants use complex mathematical calculations, similar to human circadian rhythms, to adjust their energy usage.
- Following a large-scale genome study, researchers identify some of the biological roots of migraine, a chronic neurological condition affecting as many as 15% of all humans.
- The 2013 Paris Air Show concludes, after a week of new technology demonstrations including a "green" electric airliner taxiing system, the world's first electric tiltrotor prototype, and advanced avionics and in-flight entertainment systems.
- 24 June
- Researchers from Duke University detect methane in drinking water in Pennsylvania, claiming that "serious contamination from bubbly methane is 'much more' prevalent in some water wells within 1 kilometer of gas drilling sites". The researchers note that methane levels are "an average of six times" higher and ethane levels are "23 times higher" in the water wells "closer to drilling sites, compared with those farther away."
- The 10,000th near-Earth object is discovered by astronomers at the University of Hawaii.
- 25 June – In an unprecedented discovery, astronomers detect three potentially Earthlike exoplanets orbiting a single star in the Gliese 667 system.
- 26 June
- China's Shenzhou 10 crewed spacecraft returns safely to Earth, having conducted China's longest human space mission to date.
- American scientists partially heal spinal cord injuries in paralyzed rats by transplanting nerve cells into the injury sites. These laboratory trials are hoped to be a precursor to human trials in the near future.
- Ancient horse bones dating back 700,000 years are found to contain by far the oldest preserved DNA sequence yet discovered, predating all previous finds by 500,000 years.

- 27 June
- Japanese scientists produce a healthy cloned mouse from cells contained in a single drop of blood.
- British geologists report that 1.3 quadrillion cubic feet of shale gas are present in shale formations in northern England, potentially heralding a transformation of the British energy market.
- Researchers create genetically engineered wheat strains resistant to the fungal disease stem rust, which is a constant threat to wheat crops in the developing world.
- Scientists demonstrate an optical fiber that uses "twisted light" to transmit massive amounts of information, potentially revolutionizing the field of data transfer. The prototype fiber was able to transmit data at rates of over one terabit per second.
- US and German scientists develop a simple and efficient new method for desalinating seawater, using a small electric field to separate salt from water without needing complex filter membranes.
- US and Swiss researchers develop a new form of telescopic contact lens designed to improve the vision of those with age-related macular degeneration, which previously could not be ameliorated with contact lenses.
- Molecular biologists successfully trap a ribosome in the middle of its protein-forming state, allowing them to study the precise motions it uses to translate genetic code into functional proteins. This discovery sheds new light on the basic building-blocks of life, and may allow the development of new antibiotics.
- 28 June – MIT engineers invent a handheld "X-ray vision" device which allows users to detect movement through walls.
July
- 1 July
- Neptune's moon Neptune XIV is discovered.
- The Fermi Gamma-ray Space Telescope releases new data on the highest-energy regions of the observable universe, including over 500 new gamma-ray bursts.
- 2 July
- Drinking several cups of coffee daily appears to reduce the risk of suicide in men and women by about 50%, according to a new study by Harvard School of Public Health (HSPH) researchers.
- Using computer modelling and solar data, Scottish scientists determine that the last living species on Earth in the distant future will be extremophile microbes able to survive harsh conditions.
- Microsoft develops a 3D touchscreen that uses force sensors and a robotic arm to allow users to "feel" objects that it displays.
- The first Maersk Triple E-class container ships, the largest and most energy-efficient cargo vessels yet constructed, begin sea trials.
- The two most recently discovered moons of Pluto are officially named Styx and Kerberos.

- 3 July
- In a breakthrough for regenerative medicine, Japanese scientists grow functional livers from stem cells and successfully transplant them into mice.
- It is reported that naval sonar can seriously disrupt the behavior of whales, potentially causing them to fatally beach themselves.
- Bone marrow transplants are found to remove all traces of HIV from two test patients, in conjunction with antiretroviral treatments.
- A New Zealand student designs a "skeletal" 3D-printable orthopedic cast that offers far greater lightness, cleanliness and ventilation than conventional casts, and can be personalized to suit individual patients and specific injuries.
- 4 July
- The London Array, at the time the world's largest offshore wind farm, opens in the UK.
- A US study reveals that remaining mentally and physically active in old age is key to slowing the onset of dementia.
- 5 July
- European researchers create molecular nanowires which are ultra-sensitive to ambient magnetic fields, requiring no actual magnetic materials to change their electrical conductivity. The invention, which is similar to the system used for navigation by migratory birds, could have numerous applications in electronics, from improved magnetic sensors and hard disk drives to enhanced smartphones.
- Scientists record X-ray videos of bats in flight, revealing the highly efficient skeletal motion that allows them to fly. This data could be used to design new, more efficient flying robots.
- 6 July
- The Solar Impulse aircraft completes the first cross-country flight over the United States powered entirely by solar energy.
- Scientists report that a wide variety of microbial life exists in the subglacial Antarctic Lake Vostok, which has been buried in ice for around 15 million years. Samples of the lake's water obtained by drilling were found to contain traces of DNA from over 3,000 tiny organisms.
- 8 July
- Nanoparticles of rust could be used to efficiently generate hydrogen fuel from sunlight and water, according to a scientific study.
- Researchers state that the first baby conceived with a new, cheaper, more efficient form of IVF is born healthy.

- 9 July
- Scientists develop a blood test for babies that can reportedly predict a person's long-term health and rate of ageing in later life.
- A radical new theory of the composition of the Earth's core is published. It proposes that the shape of the solid iron core is determined by the atomic structure of the different forms of iron of which it consists.
- North Carolina State University researchers demonstrate a method of 3D printing liquid metal at room temperature, forming freestanding structures which maintain their shape despite initially remaining liquid. The invention, which uses an alloy of gallium and indium, could allow electronic circuitry and even flexible wiring to be printed on demand.
- 10 July
- French scientists construct an ultra-precise optical lattice clock that misses only one second in 300 million years. The clock's measurements could form a new basis for global time standards, replacing the present generation of atomic clocks.
- The American Northrop Grumman X-47B becomes the first drone to perform an arrested landing on an aircraft carrier at sea.
- 11 July
- For the first time, astronomers determine the true colour of a distant exoplanet. HD 189733 b, a searing-hot gas giant, is said to be a vivid blue colour, most likely due to clouds of silica in its atmosphere.
- Italian scientists successfully treat the symptoms of leukodystrophy in six young children using gene therapy.
- DARPA and Boston Dynamics unveil the Atlas humanoid robot, a 6-foot (1.8 m) autonomous machine capable of a wide variety of military and disaster-response operations.
- The Canadian AeroVelo team wins the Igor Sikorsky Prize for developing a fully functional human-powered helicopter, 33 years after the competition began.
- 12 July – British engineers develop a high-velocity penetrator probe capable of surviving impact forces of 20,000 gravities. The probe could be used to punch through the icy surface of Jupiter's moon Europa to search for aquatic life.
- 15 July
- Scientists sequence the genomes of 201 microbe species in an effort to gain a more detailed understanding of Earth's microbial ecosystem.
- The Hubble Space Telescope photographs a new moon of Neptune, the 14th to be discovered so far. It is estimated to be just 12 miles (19 km) across.
- NASA engineers successfully test a rocket engine with a fully 3D-printed injector, proving that critical rocket components can be produced through 3D printing without compromising their effectiveness.
- Seismologists report that small earthquakes occur in a sequence with rapidly increasing frequency prior to a volcanic eruption. The discovery, described as a "seismic scream", could help predict future eruptions.

- 16 July
- NASA's Curiosity rover reaches a milestone in its journey across Mars, having travelled 1 kilometre (0.62 mi) since its landing in 2012.
- Researchers develop artificial peroxisomes that can reduce toxic oxygen compounds. This could lead to novel drugs that influence processes directly inside living cells.
- 17 July
- American scientists develop a method of "switching off" the extra chromosome that causes Down's syndrome, potentially offering an entirely new treatment for the condition.
- British medical researchers create an "intelligent" surgical knife with a built-in mass spectrometer that can detect cancerous tissue during operations, allowing surgeons to more accurately and effectively excise tumors without damaging healthy tissue.
- Swedish scientists create a magnesium carbonate-based material with an unparalleled surface-area-to-volume ratio and excellent water absorption abilities. The new material, dubbed "Upsalite", could have applications in many fields, including electronics, toxic waste cleanup, sanitation and medical drug delivery.
- In an unprecedented discovery, astronomers directly observe the destruction of a gas cloud larger than Earth's solar system by the supermassive black hole at the galactic core.
- Based on 34 earlier studies, researchers identify remarkable similarities between the brains of birds and humans.
- 18 July – A "giant" new genus of virus, Pandoravirus, is announced, along with two recently identified species, Pandoravirus dulcis and Pandoravirus salinus.
- 19 July
- Japan begins a clinical trial of stem cells harvested from patients' own bodies. The stem cells will be used to treat age-related macular degeneration.
- NASA scientists publish the results of a new analysis of the atmosphere of Mars, reporting a lack of methane around the landing site of the Curiosity rover. In addition, the scientists found evidence that Mars "has lost a good deal of its atmosphere over time", based on the abundance of isotopic compositions of gases, particularly those related to argon and carbon.
- Japanese researchers confirm that muon-type neutrinos can spontaneously flip to the electron type, potentially explaining the imbalance of matter and antimatter during the Big Bang.
- Harvard University medical experts report that a carefully targeted two-drug treatment could be tailored to successfully treat almost any form of cancer.
- For the third time in history, Earth is photographed from the outer solar system. NASA's Cassini spacecraft releases images of the Earth and Moon taken from the orbit of Saturn.

- 21 July
- British scientists successfully cure blindness in mice with infusions of stem cells that repaired damaged retinas. It is hoped that a similar treatment can be developed for humans.
- A private spaceflight venture announces plans to land a robotic observatory on the south pole of the Moon.
- American researchers develop a flexible, sensitive "electronic skin" that mimics real human skin by detecting and responding to different levels of pressure.
- 22 July
- Scientists report that dolphins have unique vocal names for one another, which they respond to just as humans do.
- Scientists studying data from the Large Hadron Collider report an extremely rare particle decay event, casting doubt on the scientific theory of supersymmetry.
- 23 July – Thor's hero shrew, the first known sister species to the armored shrew, is described.
- 24 July – A scientific study warns that a major release of methane from melting Arctic ice could have immense climatic and economic impacts worldwide.
- 25 July
- British scientists discover the mechanism which causes human allergy to cats. A cure for the allergy may become commercially available within five years.
- Scientists successfully implant false memories into the brains of mice. This breakthrough could lead to a fuller understanding of human memory.
- 26 July – Scientists demonstrate a GM-free process that could dramatically reduce nitrogen pollution. It allows virtually all of the world's crop species to automatically obtain up to 60% of their nitrogen requirements from air, as opposed to fertilisers.
- 28 July – A new DNA probe allows researchers to look for mutations in long sequences of up to 200 base pairs, compared to only 20 pairs using conventional methods.
- 29 July – Astronomers discover the first exoplanet orbiting a brown dwarf, 6,000 light years from Earth.
- 31 July
- An artificial human-like ear is grown in a lab, using a flexible wire frame to support tissue cultures from cows and sheep.
- New data from the Large Hadron Collider – based on measurements of the B meson – could offer the first direct hint of new physics beyond the Standard Model.
August
- 1 August
- Michigan State University reports that climate change is fueling larger and more destructive wildfires in the United States, a trend that is set to continue.
- Efficient chemical synthesis of ingenol mebutate is achieved for the first time. This compound – found in the plant genus Euphorbia – is of great interest to drug developers for its anticarcinogenic properties.
- 2 August
- The American Meteorological Society releases its peer-reviewed State of the Climate report, showing how the impacts of global warming are worsening.
- A new "super-glass" coating produced by Harvard University researchers could lead to self-cleaning, scratch-resistant windows and other surfaces.
- 5 August
- The world's first hamburger made entirely of lab-grown in-vitro meat is eaten in London.
- A Japanese company develops a reusable skin patch which can treat chronic high blood pressure by constantly releasing bisoprolol into the bloodstream. It is reported to be safer than conventional blood pressure medication, and is easier to use for patients with swallowing problems.
- Full-colour, 3D infrared images have been created by researchers, giving molecular-level chemical information of specimens in unprecedented detail.
- 7 August
- A new study of the cosmic microwave background has looked back to within 100,000 years of the Big Bang, the furthest that has yet been observed.
- A new deep brain stimulation device can simultaneously record brain activity while delivering therapy. It is hoped the automated system could reveal major insights into a range of neurological and psychological diseases.
- 8 August
- In its latest trial, a new malaria vaccine has been shown to be 100 percent effective.
- A breakthrough in tissue engineering has allowed scientists to 'grow' the first true cartilage. The researchers believe entire organs may be possible by 2025.
- 12 August – A gene linked to idiopathic focal epilepsy (IFE) has been identified by MedUni Vienna researchers.
- 14 August
- In the largest-ever analysis of cancer genomes, researchers have discovered the genetic imprints and signatures left by DNA-damaging processes that lead to cancer.
- Scientists have built a fully functional mouse heart from human tissues.
- Seagrass is 35 times more efficient at absorbing carbon than rainforests, according to research by the University of Technology, Sydney.
- 15 August
- For the first time in 35 years, a new carnivorous mammal species – the olinguito – has been discovered in the Western Hemisphere.
- NASA announces that the failing Kepler space observatory may never fully recover. New missions are being considered.
- Extreme heat waves are likely to quadruple by 2040, according to new research.
- Biologists from Tel Aviv University publish a, first of its kind, study on homosexual behavior among insect species.
- 17 August – In an unprecedented effort by ETH Zurich Laboratories, computational quantum teleportation has been achieved in solid-state circuit. Using quantum entanglement methods, researchers have teleported approximately 10,000 qubits (quantum bits) per second on a specially designed chip.
- 21 August – The lowest temperature at which single-celled organisms can live and grow is -20 °C, according to new research.
- 22 August
- A study has found more evidence that nanoparticles may be entering the human food supply, with potentially harmful effects.
- A study has found that urban environments may cause increased brain size in animals.
- NASA has released new images and a video of its planned asteroid capture mission.
- 27 August
- The previous discovery of a new chemical element with atomic number 115 (moscovium) has been confirmed at GSI by researchers from Lund University in Sweden.
- NASA reports that the Mars Curiosity rover used an Autonomous Navigation System (or "autonav" - the ability of the rover to decide for itself how to drive safely) over unknown ground for the first time.
- University of Washington researchers have performed what they believe is the first noninvasive human-to-human brain interface, with one researcher able to send a brain signal via the Internet to control the hand motions of a fellow researcher.
- 28 August
- Miniature, pea-sized human brains have been grown in the laboratory from stem cells.
- Cooling waters in the tropical Pacific Ocean appear to be a major factor in dampening global warming in recent years, scientists say.
- UK researchers have created the world's fastest spinning man-made object, achieving 600 million revolutions per minute.
- 29 August
- By reducing the action of a single gene, mTor, researchers have increased the average lifespan of mice by 20 percent. Their research also shows that the effects of aging are not uniform.
- The East Antarctic Ice Sheet could be more vulnerable to climate change than previously thought, based on a new analysis of satellite imagery going back 50 years.
- A NASA mission has revealed a new canyon – 460 miles (750 km) long and 2,600 feet (800 meters) deep in places – hidden below Greenland's ice sheet. This is longer than the Grand Canyon.
September
- 1 September – Rising global temperatures are driving crop pests to higher and lower latitudes at nearly 3 kilometres per year, threatening global food security.
- 2 September – A team of international scientists has achieved a major breakthrough in nanosensing.
- 3 September
- A new analysis indicates the amount of raw materials used to produce goods is far higher than previously thought.
- Phase I clinical trials of SAV001 – the first and only preventative HIV vaccine – have been successfully completed with no adverse effects in all patients. Antibody production was greatly boosted after vaccination.
- 5 September
- It has been confirmed that an undersea volcano in the northern Pacific is not a group of several volcanos. This makes it the largest confirmed volcano on Earth.
- Stanford researchers use DNA to assemble a transistor from graphene.
- Two leading neurology researchers claim that prion-like proteins that misfold and aggregate into harmful "seeds" are responsible for brain diseases associated with aging.
- 6 September
- The Lunar Atmosphere and Dust Environment Explorer (LADEE) is launched by NASA. It will measure the extremely thin atmosphere that surrounds the Moon.
- Researchers have developed a new method for improving the connections between stacked solar cells. It allows them to operate at concentrations of 70,000 suns worth of energy without losing much voltage as "wasted energy" or heat.
- Phase 1 clinical trials of an implantable vaccine to treat melanoma have been initiated.
- The National Institutes of Health has awarded grants of $17 million to eight research teams, with a focus on nanopore technology aimed at more accurate and efficient DNA sequencing.
- 11 September
- Three ancient rivers may once have crossed the Sahara, allowing early humans to cross from Africa into the Mediterranean about 100,000 years ago, based on a new study.
- Huge new reserves of groundwater have been found in Turkana County, northern Kenya.
- Trees are speeding up their life cycles in response to climate change, backing up the results of an earlier study.
- Rapidly melting sea ice is causing ocean acidification in the Arctic to occur at faster rates than previously forecast, with serious implications for the food web, according to new research.
- 12 September
- NASA announces that Voyager I has officially left the Solar System, having travelled since 1977.
- Americans are living longer and more healthily than ever before, according to one of the most comprehensive studies of its kind. There was a 3.8-year increase in average life expectancy during the previous two decades, with quality-adjusted life expectancy (QALE) also increasing. However, there was a notable rise in anxiety among young and middle-aged people beginning in 2001.
- 14 September – The Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA) has launched its first Epsilon rocket, a new generation of smaller and cheaper launch vehicles.
- 18 September – Orbital Sciences launches the first Cygnus spacecraft. It is designed to transport supplies to the International Space Station (ISS).
- 19 September – Scientists working with the Curiosity rover on the planet Mars report "no detection of atmospheric methane with a measured value of 0.18±0.67 ppbv corresponding to an upper limit of only 1.3 ppbv (95% confidence limit)" and, as a result, conclude that the probability of "current methanogenic microbial activity on Mars" is reduced.
- 20 September
- Researchers from Cambridge University in England have developed a new technique allowing carbon nanotube "forests" to be grown at five times the density of previous methods.
- Researchers have identified a protein involved in the spread of brain tumours.
- 22 September – Researchers have created a "blueprint" for a universal flu vaccine which they say could be available within five years.
- 23 September – A new world record solar cell efficiency of 44.7% has been achieved.
- 24 September
- The first evidence of whisper-like behavior in non-human primates has been observed.
- Astronomers have discovered the densest known galaxy, with over 10,000 stars packed into four light years.
- Long-term data shows that the Greenland Sea is warming 10 times faster than the global ocean.
- A new genetic analysis shows that the first rapid population growth of humans occurred in the Paleolithic (60,000-80,000 years ago), rather than the more recent Neolithic as previously thought.
- The Late Cretaceous period was likely ice-free, with implications for Earth's future climate, based on new research.
- 25 September
- The first mind-controlled prosthetic leg has been created.
- A new form of matter has been created that induces photons to behave like a Star Wars light-sabre.
- The first computer made entirely of carbon nanotubes has been created by Stanford University engineers. It has a 1 bit processor, runs at 1 kHz and features 178 transistors, with 10-200 nanotubes per transistor.
- 26 September
- Palaeontologists have discovered a fossil of the oldest known creature with a jaw, dating back 419 million years.
- NASA scientists report the Mars Curiosity rover detected "abundant, easily accessible" water (1.5 to 3 weight percent) in soil samples at the Rocknest region of Aeolis Palus in Gale Crater. In addition, the rover found two principal soil types: a fine-grained mafic type and a locally derived, coarse-grained felsic type. The mafic type, similar to other martian soils and martian dust, was associated with hydration of the amorphous phases of the soil. Also, perchlorates, the presence of which may make detection of life-related organic molecules difficult, were found at the Curiosity rover landing site (and earlier at the more polar site of the Phoenix lander) suggesting a "global distribution of these salts". NASA also reported that Jake M rock, a rock encountered by Curiosity on the way to Glenelg, was a mugearite and very similar to terrestrial mugearite rocks.
- 27 September
- The FDA approves the first artificial pancreas.
- Nanoscale resolution MRI has been experimentally achieved.
- The first document from the IPCC Fifth Assessment Report – Working Group I's summary for policymakers – is released. It states that warming of the global climate system is "unequivocal", with a 95% probability that humans are the main cause.
- 30 September
- Astronomers have created the first cloud map of an exoplanet, Kepler-7b.
- The first commercial-scale carbon capture and mineralization plant begins construction in the United States. When completed in 2014, it will capture 300,000 tons of CO2 annually.
October
- 1 October – New fossils of pollen grains show that flowering plants evolved 100 million years earlier than previously thought, in the Early Triassic (252 to 247 million years ago) or even earlier.
- 3 October
- Environmental impacts on the world's oceans are even worse than previously thought, according to a new report.
- Using genetic engineering, researchers at the University of California, Los Angeles, have boosted production of ethanol biofuel by 50 percent.
- 4 October – Researchers from MIT have created self-assembling robots, based on small cubes that can propel themselves and snap together to form shapes.
- 6 October – Giant channels up to 250m tall have been discovered beneath Antarctica, stretching for hundreds of kilometres. Researchers say these will help in modelling the future stability and dynamics of the ice sheet.
- 7 October
- The Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine has been awarded to James E. Rothman, Randy W. Schekman and Thomas C. Südhof, for their work on how vesicles fuse with cell membranes, releasing their contents.
- It is reported that researchers at the National Ignition Facility in California produced more energy from a fusion reaction than the fuel absorbed in igniting it – the first time this has been achieved by researchers anywhere in the world.
- A new study concludes that research to delay aging would have greater social and economic benefits than advances in cancer, heart disease and other individual diseases.
- 8 October
- The Nobel Prize in Physics has been awarded to François Englert and Peter Higgs "for the theoretical discovery of a mechanism that contributes to our understanding of the origin of mass of subatomic particles, and which recently was confirmed through the discovery of the predicted fundamental particle, by the ATLAS and CMS experiments at CERN's Large Hadron Collider".
- Researchers in Germany have taken a major step towards using graphene in solar cells, which could boost their efficiency. The material was found to retain its properties even when coated with silicon.
- 9 October
- The Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Arieh Warshel, Martin Karplus and Michael Levitt "for the development of multiscale models for complex chemical systems".
- A new microscopic technique allows researchers to image structures as small as 80 nm anywhere inside a cell.
- 10 October – Researchers have discovered the first chemical to prevent all brain cell death from prion disease in mice. This could lead to drug targets for a range of neurodegenerative conditions in humans - including Alzheimer's, Parkinson's and Huntington's disease.
- 11 October
- The Nobel Peace Prize has been awarded to the Organisation for the Prohibition of Chemical Weapons (OPCW) and the "conventions under which it was founded in 1997" because they, according to the award citation, "have defined the use of chemical weapons as a taboo under international law. Recent events in Syria, where chemical weapons have again been put to use, have underlined the need to enhance the efforts to do away with such weapons."
- The Graphene Flagship – a ten-year initiative with a billion euros of funding – is launched in Gothenburg, Sweden.
- 14 October – The first fossil of a mosquito with definitive evidence of blood has been discovered in northwestern Montana. The find dates back to the Eocene, some 46 million years ago (the fossil provides only evidence of blood, but not blood itself, so there is no DNA or anything cloneable).
- 15 October – Red Bull Stratos releases POV video of Felix Baumgartner skydiving jump from the stratosphere (127,851 ft) on 14 October 2012.
- 16 October
- Russian authorities raise a large fragment, 654 kg (1,442 lb) total weight, of the Chelyabinsk meteor, a Near-Earth asteroid that entered Earth's atmosphere over Russia on 15 February 2013, from the bottom of Chebarkul lake.
- Researchers have identified 127 repeatedly mutated genes that appear to drive the development and progression of a range of tumors in the body.
- 17 October
- A new fossil discovery suggests that Homo habilis, Homo rudolfensis and Homo erectus may all have been part of a single species that later evolved into humans.
- Researchers have shown that a fundamental reason for sleep is to clean the brain of toxins. This is achieved by brain cells shrinking to create gaps between neurons, allowing fluid to wash through.
- Using data accumulated over 10 years, researchers have estimated there are 390 billion trees in the Amazon rainforest, divided into 16,000 different species.
- Geneticist Bryan Sykes and his team at Oxford University report that DNA analysis of presumed Yeti (or "Abominable Snowman") samples may have come from a hybrid species of bear produced from a mating between a brown bear and a polar bear. According to Sykes, "I think this bear, which nobody has seen alive, may still be there and may have quite a lot of polar bear in it. It may be some sort of hybrid and if its behaviour is different from normal bears, which is what eyewitnesses report, then I think that may well be the source of the mystery and the source of the legend."
- 18 October – Researchers have discovered a source of gut stem cells that can repair a type of inflammatory bowel disease when transplanted into mice.
- 21 October – In the Amazon, droughts like that of 2005 may become the norm by 2100, according to a new study that claims the IPCC has underestimated the impacts on the southern part of the rainforest.
- 22 October – Astronomers have discovered the 1,000th known exoplanet.
- 23 October
- A new way of locating metal deposits including gold has been discovered by researchers in Australia. The presence of tiny particles in a eucalyptus tree's foliage can indicate that these resources are present deep underground.
- Astronomers have discovered the most distant galaxy to date.
- 25 October
- The New Horizons probe is now within 5 AU of Pluto.
- Temperatures in the Eastern Arctic are now the highest since the beginning of the last ice age 120,000 years ago, lying "well outside the range of natural variability", according to US researchers.
- 27 October
- An international team of researchers has doubled the known number of genes linked to Alzheimers to 21.
- A breakthrough in artificial intelligence has been achieved, with a new software algorithm capable of solving CAPTCHAs.
- 28 October – The commercial viability of shale oil and gas has been questioned at a conference organised by the Geological Society of America.
- 30 October – Doctors in China have regrown the face of a 17-year-old girl with burn injuries, using tissue from her chest.
- 31 October – A new study adds weight to the idea that the oceans have absorbed some of the excess heat from recent global warming.
November
- 3 November – A total solar eclipse occurs.
- 4 November – Astronomers report, based on Kepler space mission data, that there could be as many as 40 billion Earth-sized planets orbiting in the habitable zones of sun-like stars and red dwarf stars within the Milky Way Galaxy. 11 billion of these estimated planets may be orbiting sun-like stars. The nearest such planet may be 12 light-years away, according to the scientists.
- 5 November – India launches its first Mars probe, Mangalyaan.
- 6 November
- Researchers have found a way to shrink the volume of nuclear waste by 90 percent.
- Japanese researchers have demonstrated multi-component nanoparticles that combine the properties of different materials.
- People care more about the longer term when they make decisions in natural environments as opposed to urban, according to research by VU University Amsterdam.
- 8 November – Scientists report the discovery of what may be the oldest complete fossils on Earth - a tiny microbial mat associated with sandstone rock in western Australia estimated to be 3.48 billion years old.
- 9 November – A major iceberg measuring 700 square kilometers, roughly the size of Singapore, has broken away from West Antarctica.
- 11 November
- A new imaging technique can help to identify people at high risk of a heart attack.
- Using nanotechnology, researchers at Columbia University have created the world's smallest FM radio.
- 13 November
- Globally, 2013 is likely to be among the top 10 hottest years since records began, according to a provisional statement from the World Meteorological Organization.
- NASA announces the names of two features on Mars important to two active Mars exploration rovers in honor of planetary scientist Bruce C. Murray (1931-2013): "Murray Ridge", an uplifted crater that the Opportunity rover is exploring, and "Murray Buttes", an entryway the Curiosity rover will traverse on its way to Mount Sharp.
- NASA has produced a video of how Mars may have appeared 4 billion years ago, with blue skies and water.
- 14 November – Globally, there was a net loss of 1.5 million sq ft of forest between 2000 and 2012, based on 650,000 high-resolution satellite images.
- 15 November – A fragile quantum memory state has been held stable at room temperature for a "world record" 39 minutes, 100 times longer than ever before.
- 17 November
- Researchers have made the first battery electrode that heals itself, repairing imperfections within a few hours.
- The first "mini-kidneys" have been grown from human stem cells.
- 18 November
- The MAVEN spacecraft, part of NASA's Mars Scout Program, is launched successfully.
- Global CO2 emissions are on track to reach 36 billion tonnes in 2013, according to the Global Carbon Project.
- 20 November
- A new 3D printing process developed at the University of Southern California could reduce production time from hours to minutes.

- A new volcanic island rose from the Pacific Ocean, in the Volcano Islands arc, and was provisionally named Niijima
- 21 November
- NASA releases detailed data about a powerful gamma-ray burst, designated GRB 130427A, that was observed on 27 April 2013.
- The IceCube Neutrino Observatory has made the first discovery of very high energy neutrinos on Earth which had originated from beyond our Solar System.
- A potential new compound to treat osteoporosis has shown promising results in mouse experiments.
- 22 November
- The Swarm mission is launched by ESA. It will map the Earth's magnetic field in unprecedented detail.
- Researchers at Bonn University have identified an immune gene in humans that originated from Neanderthals.
- Paleontologists have described a newly found dinosaur, Siats meekerorum, that lived 98 million years ago in the Late Cretaceous. Based on analysis of a juvenile 30 ft specimen, the researchers say the adult version could have reached 40 ft (12 meters) in length – second only to Tyrannosaurus rex in size, and holding back the dominance of that species until later in the epoch.
- 24 November
- Even if CO2 emissions stop, global warming will continue for centuries, according to a study by Princeton University.
- Methane release from the Arctic seafloor is double previous estimates, new research has shown.
- 25 November – NASA reports that the Curiosity rover on Mars has resumed full science operations, with no apparent loss of capability, after completing the diagnosis of an electrical problem first observed on 17 November. Apparently, an internal short in the rover's power source, the Multi-Mission Radioisotope Thermoelectric Generator, caused an unusual and intermittent decrease in a voltage indicator on the rover.
- 28 November – The comet C/2012 S1 (ISON) passed roughly 1,100,000 kilometres (680,000 miles) above the Sun's surface. Although it was highly anticipated that the comet would be visible to the naked eye on Earth once it orbited the Sun, it became increasingly evident that it had vaporized as it made its approach. Hours after it passed behind the Sun, a part of the comet re-emerged, though significantly smaller. Over the next 24 hours, it too, faded.
- 29 November – Scientists report Comet ISON may have survived its trip around the Sun.
December
- 1 December – China launches the Chang'e 3 lunar rover mission, with a planned landing on 16 December.
- 2 December
- A study of nearly 1,000 brain scans has revealed striking differences between men and women.
- The CIOC (NASA Comet ISON Observing Campaign) announces that Comet ISON has fully disintegrated. The Hubble Space Telescope failed to detect fragments of ISON on 18 December 2013. On 8 May 2014, a detailed examination of the comet disintegration was published, suggesting that the comet fully disintegrated hours before perihelion.
- 3 December – The Hubble Space Telescope has found evidence of water in the atmospheres of five distant exoplanets: HD 209458b, XO-1b, WASP-12b, WASP-17b and WASP-19b.
- 4 December
- Researchers have discovered that a protein, PC7, plays an important role in anxiety disorders and trauma.
- Scientists report the results of the oldest human DNA found. The DNA is from a 400,000-year-old hominin femur bone fossil uncovered in Spain and matches the DNA of extinct human Denisovans that lived thousands of miles away in Siberia.
- Researchers at the University of Southampton have identified undersea regions that could store huge volumes of sequestered CO2, potentially helping to reverse climate change.
- 5 December – Researchers have used a human gut microbe to reverse autism-like symptoms in mice.
- 8 December – A new way of extracting hydrogen from rocks and water, potentially offering a new green energy source, has been demonstrated by the University of Lyon.
- 9 December
- NASA scientists report that the planet Mars had a large freshwater lake (which could have been a hospitable environment for microbial life) based on evidence from the Curiosity rover studying Aeolis Palus near Mount Sharp in Gale Crater.
- A newly discovered greenhouse gas, perfluorotributylamine, has been shown to have 7,100 times the heat-trapping ability of CO2.
- 10 December – A new record low temperature on Earth has been recorded, with NASA satellite data showing -94.7 °C (-135.8 °F) in a region of East Antarctica. The previous record had been -89.2 °C (-128.6 °F), set in 1983 at Vostok Station.
- 11 December
- The supervolcano that lies beneath Yellowstone National Park in the US has a magma chamber that is 2.5 times bigger than earlier estimates suggested.
- Ice loss from the West Antarctic Ice Sheet is accelerating, based on the latest data from CryoSat-2. Over 150 cubic km of ice is now melting into the sea each year.
- NASA reports the detection of "clay-like minerals" (specifically, phyllosilicates), often associated with organic materials, on the icy crust of Europa, moon of Jupiter. The presence of the minerals may have been the result of a collision with an asteroid or comet according to the scientists.
- A new hydrogel scaffold has been developed for craniofacial bone tissue regeneration, which turns from a liquid to gel in the body, then liquefies again for removal.
- 12 December
- NASA announces, based on studies with the Hubble Space Telescope, that water vapor plumes were detected on Europa, moon of Jupiter, and were similar to water vapor plumes detected on Enceladus, moon of Saturn.
- A new drug has been shown to reduce the risk of breast cancer in post-menopausal women by 53 percent.
- Researchers have achieved a five-fold increase in the lifespan of Caenorhabditis elegans, the equivalent of a human reaching 400–500 years of age.
- 13 December – Astronomers at the University College London report the detection of noble molecules in outer space for the first time. Argon-36, in the form of argon hydride, was found in cosmic dust associated with the Crab nebula supernova.
- 14 December – The uncrewed Chinese lunar rover Chang'e 3 lands on the Moon, making China the third country to achieve a soft landing there.
- 16 December – An international team of researchers reports evidence that Neanderthals practiced burial behavior and intentionally buried their dead.
- 18 December
- Scientists report, for the first time, the entire genome of a Neanderthal, an extinct species of humans. The genome was extracted from the toe bone of a 130,000-year-old Neanderthal found in a Siberian cave.
- Astronomers have spotted what appears to be the first known "exomoon", located 1,800 light years away.
- 19 December
- The European Space Agency's Gaia space telescope is launched.
- Researchers at Harvard Medical School have achieved a major breakthrough in the study of aging. By using a chemical that occurs naturally in the human body, it was possible to restore tissues in two-year-old mice to a much younger state.
- 20 December
- NASA reports that the Curiosity rover has successfully upgraded, for the third time since landing, its software programs and is now operating with version 11. The new software is expected to provide the rover with better robotic arm and autonomous driving abilities. Due to wheel wear, a concern to drive more carefully, over the rough terrain the rover is currently traveling on its way to Mount Sharp, was also reported.
- French Professor Alain Carpentier has developed the first self-regulating artificial heart, using biomaterials and electronic sensors. The device was successfully implanted by a team at the Georges Pompidou European Hospital in Paris.
- 22 December
- A massive underground reservoir of meltwater has been discovered below Greenland, storing liquid water all year round and covering 27,000 square miles. This has implications for sea level rises.
- Solar activity is not a key cause of recent climate change, a new study shows.
- 30 December – Earth's crust was unstable during the Archean era and would have "dripped" down into the mantle, which was much hotter than today, according to new research.
- 31 December – NASA reports that clouds may have been detected in the atmospheres of several exoplanets; specifically, GJ 436 b and GJ 1214 b. Earlier, on 31 September, clouds were reported found, for the first time on an exoplanet, on Kepler-7b.
Awards
Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences
- Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences: Cornelia I. Bargmann, David Botstein, Lewis C. Cantley, Hans Clevers, Titia de Lange, Napoleone Ferrara, Eric S. Lander, Charles L. Sawyers, Robert A. Weinberg, Shinya Yamanaka and Bert Vogelstein
Nobel Prize
- Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine: James E. Rothman, Randy W. Schekman and Thomas C. Südhof
- Nobel Prize in Physics: François Englert and Peter Higgs
- Nobel Prize in Chemistry: Martin Karplus, Michael Levitt and Arieh Warshel
Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering
- Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering: Marc Andreessen, Tim Berners-Lee, Vint Cerf, Bob Kahn and Louis Pouzin
UNESCO Young Scientist Awards/Michel Batisse Award
- UNESCO Young Scientist Awards and Michel Batisse Award for Biosphere Reserve Management: Julio Blas Garcia, Angela Camargo, Bilal Habib, Hilaire Kouakou, Atieh Kazemi Mojarad and Claudia Munera
Other
Deaths
January
- 6 January – Paul Grundy, Australian structural engineer (born 1935).
- 8 January – Percy White, British chemist and nuclear scientist, contributor to Britain's first nuclear bomb (born 1916).
- 9 January – Brigitte Askonas, British immunologist (born 1923).
- 11 January – Aaron Swartz, American computer programmer and Internet hactivist, suicide (born 1986).
- 14 January – Andreas Raab, German computer scientist (born 1968).
- 18 January – Jim Horning, American computer scientist (born 1942).
- 19 January – Basil Hirschowitz, South African-American gastroenterologist (born 1925).
- 21 January
- Donald Hornig, American Manhattan Project chemist and explosives expert (born 1920).
- Ahmet Mete Işıkara, Turkish geophysicist (born 1941).
- 28 January – Xu Liangying, Chinese physicist (born 1920).
February

- 8 February – Nevin S. Scrimshaw, American food scientist and nutritionist (born 1918).
- 12 February – Reginald Turnill, British BBC science and spaceflight correspondent (born 1915).
- 18 February
- Jerry Buss, American chemist and businessman (born 1933).
- Godfrey Hewitt, British biologist and geneticist (born 1940).
- 19 February – Robert Coleman Richardson, American physicist, joint winner of the 1996 Nobel Prize in Physics (born 1937).
- 20 February – David S. McKay, American astrobiologist (born 1936).
- 25 February – C. Everett Koop, American surgeon and public health official (born 1916).
- 28 February – Donald A. Glaser, American physicist, winner of the 1960 Nobel Prize in Physics (born 1926).
March
- 4 March – Hobart Muir Smith, American herpetologist (born 1912).
- 10 March – Ian Munro Ross, British-born American electrical engineer and transistor pioneer (born 1927).
- 15 March – Kallam Anji Reddy, Indian chemical engineer and pharmaceutical entrepreneur (born 1940).
- 16 March – Jamal Nazrul Islam, Bangladeshi physicist and cosmologist (born 1939).
- 21 March – Cornelis H. A. Koster, Dutch computer scientist (born 1943).
- 24 March
- Mary Gillham, British naturalist (born 1921).
- Gury Marchuk, Russian physicist and mathematician (born 1925).

- 27 March – Yvonne Brill, Canadian rocket scientist (born 1924).
- 28 March
- George E. P. Box, British-born American statistician (born 1919).
- John Findlater, Scottish meteorologist (born 1926).
April
- 8 April – Frank Panton, British military scientist and bomb disposal expert (born 1923).
- 9 April – Paolo Soleri, Italian architect and ecologist, pioneer of the arcology concept (born 1919).
- 10 April – Sir Robert Geoffrey Edwards, British physiologist and pioneer in in-vitro fertilisation, winner of the 2010 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (born 1925).
- 15 April – Benjamin Fain, Ukrainian-born Israeli physicist and dissident (born 1930).
- 19 April
- François Jacob, French biologist, winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (born 1920).

19 April 2013: François Jacob, a Nobel Prize-winning French biologist, dies aged 92. - Kenneth Appel, American mathematician (born 1932).
- François Jacob, French biologist, winner of the 1965 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (born 1920).
- 21 April – Shakuntala Devi, Indian mathematician (born 1929).
- 22 April
- Struther Arnott, Scottish molecular biologist and chemist (born 1934).
- Benjamin Milstein, British cardiothoracic surgeon and heart surgery pioneer (born 1918).
- 28 April – John C. Reynolds, American computer scientist (born 1935).
May
- 3 May – David Morris Kern, American pharmacist (born 1909).
- 4 May – Christian de Duve, English-born Belgian biologist and biochemist, co-recipient of the 1974 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine (born 1917).
- 10 May – Boicho Kokinov, Bulgarian cognitive scientist (born 1960).
- 11 May – Joe Farman, British geophysicist who worked for the British Antarctic Survey (born 1930).
- 12 May – George William Gray, Scottish chemist who discovered stable liquid crystal materials leading to the development of liquid crystal displays (born 1926).
- 16 May
- Heinrich Rohrer, Swiss physicist and nanotechnologist (born 1933).
- Frank Nigel Hepper, English botanist (born 1929).
- 29 May – Ludwig G. Strauss, German medical radiologist (born 1949).
- 31 May – Gerald E. Brown, American theoretical physicist (born 1926).
June
- 1 June – Hanfried Lenz, German mathematician (born 1916).
- 6 June – Jerome Karle, American chemist, joint winner of the 1985 Nobel Prize in Chemistry (born 1918).
- 12 June – Michael Kasha, American chemist and biophysicist (born 1920).
- 15 June – Kenneth G. Wilson, American physicist, winner of the 1982 Nobel Prize in Physics (born 1936).
- 16 June – James Massey, American electrical engineer, information theorist and cryptographer (born 1934).
- 20 June – Wu Zhengyi, Chinese botanist (born 1916).
- 21 June
- Zhang Guangdou, Chinese hydraulic engineer and member of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (born 1912).
- James P. Gordon, American physicist (born 1928).
- 22 June – Sergio Focardi, Italian physicist (born 1932).
- 24 June – James Martin, British computer scientist, author and futurist (born 1933).
- 29 June – Margherita Hack, Italian astrophysicist (born 1922).

July
- 2 July
- Douglas Engelbart, American scientist and computer pioneer, inventor of the computer mouse (born 1925).
- Anthony Llewellyn, Welsh-born American chemist and NASA astronaut candidate (born 1933).
- 8 July – Rubby Sherr, American nuclear physicist and Manhattan Project participant (born 1913).
- 9 July – Masao Yoshida, Japanese nuclear engineer who was involved in tackling the Fukushima Daiichi nuclear disaster (born 1955).
- 11 July – Milton Silveira, American aerospace engineer and NASA project manager (born 1929).
- 12 July
- Amar Bose, Indian-American electrical engineer, acoustics expert and founder of Bose Corporation (born 1929).
- Elaine Morgan, Welsh evolutionary theorist and author (born 1920).
- 15 July – John T. Riedl, American computer scientist (born 1962).
- 16 July – Yuri Vasilyevich Prokhorov, Russian mathematician (born 1929).
- 26 July – Obaid Siddiqi, Indian biologist (born 1932).
- 30 July – Godfrey Stafford, British physicist (born 1920).
August
- 5 August – Lin Chieh-liang, Taiwanese toxicologist and public health expert (born 1958).
- 27 August – David Barker, English epidemiologist (born 1938).
September
- 12 September – Ray Dolby, audio pioneer, invented the Dolby noise-reduction system and surround sound (born 1933).
- 16 September – George Hockham, English electrical engineer (born 1938)
- 23 September – Robert C. Stebbins, American herpetologist known for popular field guides (born 1915).
- 26 September – Harold Agnew, American physicist, worked on the Manhattan Project (born 1921).
October
- 2 October – Abraham Nemeth, American mathematician and inventor, created the Braille math code. (born 1918).
- 10 October – Scott Carpenter, the second American astronaut to orbit the Earth. (born 1925).
- 19 October – William C. Lowe, American businessman, manager of development of the IBM PC.
November
- 19 November – Frederick Sanger, British biochemist and laureate of Nobel Prize in Chemistry (1958, 1980). (born 1918).
- 21 November – Fred Kavli, Norwegian-born American business executive, inventor, and philanthropist (born 1927).
December
- 18 December – William T. Greenough, American neuroscientist. (born 1944).
See also
References
External links
- "A science news preview of 2013". BBC. 30 December 2012. Retrieved 26 July 2013.
- Science obituaries in The Guardian
- Science obituaries in The Daily Telegraph
- Science obituaries at Legacy.com