Barton–Zard reaction
The Barton–Zard reaction is a route to pyrrole derivatives via the reaction of a nitroalkene with an α-isocyanide under basic conditions. It is named after Derek Barton and Samir Zard who first reported it in 1985.

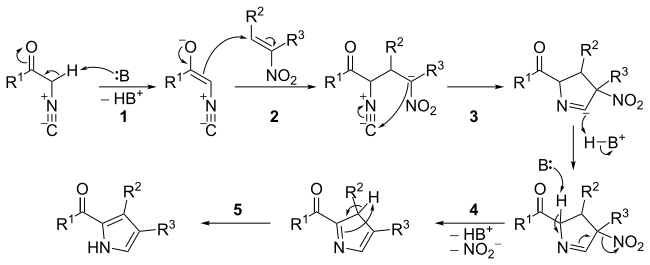
Mechanism
The mechanism consists of five steps:
- Base catalyzed carbonyl enolization of the α-isocyanide.
- Michael-type addition between the α-isocyanide carbonyl enolate and the nitroalkene.
- 5-endo-dig cyclization (see: Baldwin's rules).
- Base catalyzed elimination of the nitro group.
- Tautomerization leading to aromatisation.
Scope
The nitro compound may be aromatic rather than just an alkene. The reaction has been used for the synthesis of polypyrroles, including porphyrins, as well as dipyrromethenes such as BODIPY.