Conversion of scales of temperature
This is a collection of temperature conversion formulas and comparisons among eight different temperature scales, several of which have long been obsolete.
Temperatures on scales that either do not share a numeric zero or are nonlinearly related cannot correctly be mathematically equated (related using the symbol =), and thus temperatures on different scales are more correctly described as corresponding (related using the symbol ≘).
Celsius scale
Kelvin scale
Fahrenheit scale
Rankine scale
Delisle scale
Newton scale
Réaumur scale
Rømer scale
Conversion calculator
Comparison values chart
Comparison of temperature scales
Graphical representation
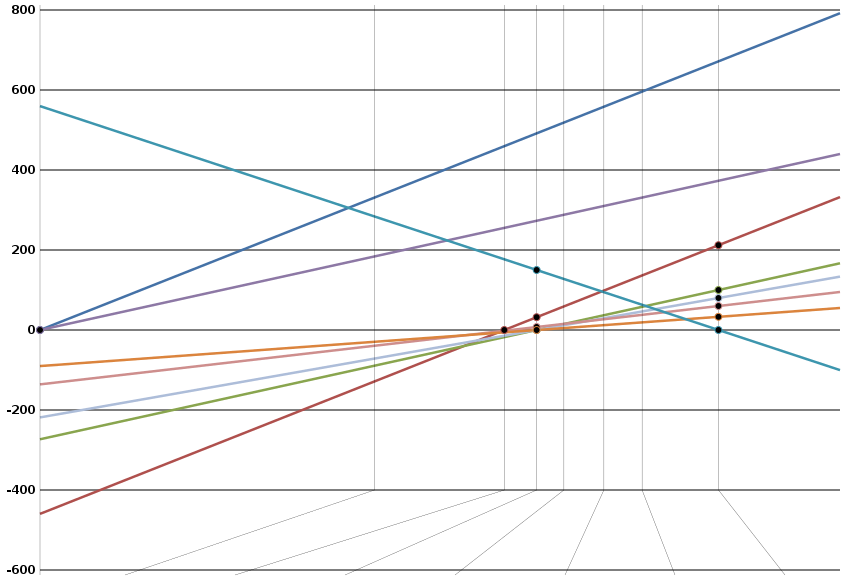 | Rankine (°R) | |||||||||
| Kelvin (K) | ||||||||||
| Fahrenheit (°F) | ||||||||||
| Celsius (°C) Réaumur (°Ré) Rømer (°Rø) Newton (°N) | ||||||||||
| Delisle (°D) | ||||||||||
| Absolute zero | Lowest recorded surface temperature on Earth | Fahrenheit's ice/water/salt mixture | Melting point of ice (at standard pressure) | Average surface temperature on Earth (15 °C) | Average human body temperature (37 °C) | Highest recorded surface temperature on Earth | Boiling point of water (at standard pressure) | |||
Conversion table between the different temperature units








Converting units of temperature differences
Converting units of temperature differences (also referred to as temperature deltas) is not the same as converting absolute temperature values, and different formulae must be used.
To convert a delta temperature from degrees Fahrenheit to degrees Celsius, the formula is {ΔT}°F =9/5{ΔT}°C.
To convert a delta temperature from degrees Celsius to kelvin, it is 1:1 ({ΔT}°C = {ΔT}K).