Star network
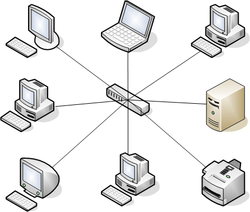
A star network is an implementation of a spoke–hub distribution paradigm in computer networks. In a star network, every host is connected to a central hub. In its simplest form, one central hub acts as a conduit to transmit messages. The star network is one of the most common computer network topologies.
Network
The hub and hosts, and the transmission lines between them, form a graph with the topology of a star. Data on a star network passes through the hub before continuing to its destination. The hub manages and controls all functions of the network. It also acts as a repeater for the data flow. In a typical network the hub can be a network switch, Ethernet hub, wireless access point or a router
The star topology reduces the impact of a transmission line failure by independently connecting each host to the hub. Each host may thus communicate with all others by transmitting to, and receiving from, the hub. The failure of a transmission line linking any host to the hub will result in the isolation of that host from all others, but the rest of the network will be unaffected.
The star configuration is commonly used with twisted pair cable and optical fiber cable. However, it can also be used with coaxial cable as in, for example, a video router.
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages
- If one node or its connection fails, it does not affect the other nodes.
- Devices can be added or removed without disturbing the network.
- Works well under heavy load.
- Appropriate for a large network.
Disadvantages
- Expensive due to the number and length of cables needed to wire each host to the central hub.
- The central hub is a single point of failure for the network.
- Each device needs a separate cable connection to the central hub, leading to higher cable usage.
- The number of devices is limited by the capacity of the central hub.