Portal:Economics
Portal maintenance status: (December 2018)
|
Introduction
Economics (/ˌɛkəˈnɒmɪks, ˌiːkə-/) is a social science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services.
Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. (Full article...)
Selected general articles
- Image 1
Wassily Wassilyevich Leontief (Russian: Васи́лий Васи́льевич Лео́нтьев; August 5, 1905 – February 5, 1999), was a Soviet-American economist known for his research on input–output analysis and how changes in one economic sector may affect other sectors.
Leontief won the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1973, and four of his doctoral students have also been awarded the prize (Paul Samuelson 1970, Robert Solow 1987, Vernon L. Smith 2002, Thomas Schelling 2005). (Full article...) - Image 2
Tjalling Charles Koopmans (August 28, 1910 – February 26, 1985) was a Dutch-American mathematician and economist. He was the joint winner with Leonid Kantorovich of the 1975 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences for his work on the theory of the optimum allocation of resources. Koopmans showed that on the basis of certain efficiency criteria, it is possible to make important deductions concerning optimum price systems. (Full article...) - Image 3Ecological economics, bioeconomics, ecolonomy, eco-economics, or ecol-econ is both a transdisciplinary and an interdisciplinary field of academic research addressing the interdependence and coevolution of human economies and natural ecosystems, both intertemporally and spatially. By treating the economy as a subsystem of Earth's larger ecosystem, and by emphasizing the preservation of natural capital, the field of ecological economics is differentiated from environmental economics, which is the mainstream economic analysis of the environment. One survey of German economists found that ecological and environmental economics are different schools of economic thought, with ecological economists emphasizing strong sustainability and rejecting the proposition that physical (human-made) capital can substitute for natural capital (see the section on weak versus strong sustainability below).
Ecological economics was founded in the 1980s as a modern discipline on the works of and interactions between various European and American academics (see the section on History and development below). The related field of green economics is in general a more politically applied form of the subject. (Full article...) - Image 4
Joan Violet Robinson FBA (née Maurice; 31 October 1903 – 5 August 1983) was a British economist known for her wide-ranging contributions to economic theory. One of the most prominent economists of the century, Robinson incarnated the "Cambridge School" in most of its guises in the 20th century. She started out as a Marshallian, became one of the earliest and most ardent Keynesians after 1936, and ended up as a leader of the neo-Ricardian and post-Keynesian schools. (Full article...) - Image 5In macroeconomics, chartalism is the theory of money that money originated historically with states' attempts to direct economic activity rather than as a spontaneous solution to the problems with barter or as a means with which to tokenize debt, and that fiat currency has value in exchange because of sovereign power to levy taxes on economic activity payable in the currency they issue. (Full article...)
- Image 6The Austrian school is a heterodox school of economic thought that advocates strict adherence to methodological individualism, the concept that social phenomena result primarily from the motivations and actions of individuals along with their self interest. Austrian-school theorists hold that economic theory should be exclusively derived from basic principles of human action.
The Austrian school originated in 1871 in Vienna with the work of Carl Menger, Eugen von Böhm-Bawerk, Friedrich von Wieser, and others. It was methodologically opposed to the Historical school, in a dispute known as Methodenstreit, or methodology quarrel. Current-day economists working in this tradition are located in many countries, but their work is still referred to as Austrian economics. Among the theoretical contributions of the early years of the Austrian school are the subjective theory of value, marginalism in price theory and the formulation of the economic calculation problem. (Full article...) - Image 7

Georgist campaign button from the 1890s in which the cat on the badge refers to a slogan "Do you see the cat?" to draw analogy to the land question
Georgism, in modern times also called Geoism, and known historically as the single tax movement, is an economic ideology holding that people should own the value that they produce themselves, while the economic rent derived from land—including from all natural resources, the commons, and urban locations—should belong equally to all members of society. Developed from the writings of American economist and social reformer Henry George, the Georgist paradigm seeks solutions to social and ecological problems based on principles of land rights and public finance that attempt to integrate economic efficiency with social justice.
Georgism is concerned with the distribution of economic rent caused by land ownership, natural monopolies, pollution rights, and control of the commons, including title of ownership for natural resources and other contrived privileges (e.g., intellectual property). Any natural resource that is inherently limited in supply can generate economic rent, but the classical and most significant example of land monopoly involves the extraction of common ground rent from valuable urban locations. Georgists argue that taxing economic rent is efficient, fair, and equitable. The main Georgist policy recommendation is a tax assessed on land value, arguing that revenues from a land value tax (LVT) can be used to reduce or eliminate existing taxes (such as on income, trade, or purchases) that are unfair and inefficient. Some Georgists also advocate for the return of surplus public revenue to the people by means of a basic income or citizen's dividend. (Full article...) - Image 8

Thorstein Bunde Veblen (/ˈθɔːrstaɪn ˈvɛblən/; July 30, 1857 – August 3, 1929) was an American economist and sociologist who, during his lifetime, emerged as a well-known critic of capitalism.
In his best-known book, The Theory of the Leisure Class (1899), Veblen coined the concepts of conspicuous consumption and conspicuous leisure. Veblen laid the foundation for the perspective of institutional economics. Contemporary economists still theorize Veblen's distinction between "institutions" and "technology", known as the Veblenian dichotomy. (Full article...) - Image 9Institutional economics focuses on understanding the role of the evolutionary process and the role of institutions in shaping economic behavior. Its original focus lay in Thorstein Veblen's instinct-oriented dichotomy between technology on the one side and the "ceremonial" sphere of society on the other. Its name and core elements trace back to a 1919 American Economic Review article by Walton H. Hamilton. Institutional economics emphasizes a broader study of institutions and views markets as a result of the complex interaction of these various institutions (e.g. individuals, firms, states, social norms). The earlier tradition continues today as a leading heterodox approach to economics.
"Traditional" institutionalism rejects the reduction of institutions to simply tastes, technology, and nature (see naturalistic fallacy). Tastes, along with expectations of the future, habits, and motivations, not only determine the nature of institutions but are limited and shaped by them. If people live and work in institutions on a regular basis, it shapes their world views. Fundamentally, this traditional institutionalism (and its modern counterpart institutionalist political economy) emphasizes the legal foundations of an economy (see John R. Commons) and the evolutionary, habituated, and volitional processes by which institutions are erected and then changed (see John Dewey, Thorstein Veblen, and Daniel Bromley). Institutional economics focuses on learning, bounded rationality, and evolution (rather than assuming stable preferences, rationality and equilibrium). It was a central part of American economics in the first part of the 20th century, including such famous but diverse economists as Thorstein Veblen, Wesley Mitchell, and John R. Commons. Some institutionalists see Karl Marx as belonging to the institutionalist tradition, because he described capitalism as a historically bounded social system; other institutionalist economists[who?] disagree with Marx's definition of capitalism, instead seeing defining features such as markets, money and the private ownership of production as indeed evolving over time, but as a result of the purposive actions of individuals. (Full article...) - Image 10
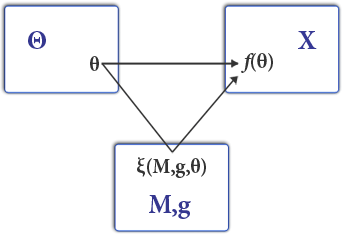
The upper-left space depicts the type space and the upper-right space X the space of outcomes. The social choice function
maps a type profile to an outcome. In games of mechanism design, agents send messages
in a game environment
. The equilibrium in the game
can be designed to implement some social choice function
.
Mechanism design (sometimes implementation theory or institution design) is a branch of economics and game theory. It studies how to construct rules—called mechanisms or institutions—that produce good outcomes according to some predefined metric, even when the designer does not know the players' true preferences or what information they have. Mechanism design thus focuses on the study of solution concepts for a class of private-information games.
Mechanism design has broad applications, including traditional domains of economics such as market design, but also political science (through voting theory). It is a foundational component in the operation of the internet, being used in networked systems (such as inter-domain routing), e-commerce, and advertisement auctions by Facebook and Google. (Full article...) - Image 11

Piero Sraffa FBA (5 August 1898 – 3 September 1983) was an influential Italian political economist who served as lecturer of economics at the University of Cambridge. His book Production of Commodities by Means of Commodities is taken as founding the neo-Ricardian school of economics. (Full article...) - Image 12Supply-side economics is a macroeconomic theory postulating that economic growth can be most effectively fostered by lowering taxes, decreasing regulation, and allowing free trade. According to supply-side economics theory, consumers will benefit from greater supply of goods and services at lower prices, and employment will increase. Supply-side fiscal policies are designed to increase aggregate supply, as opposed to aggregate demand, thereby expanding output and employment while lowering prices. Such policies are of several general varieties:
- Investments in human capital, such as education, healthcare, and encouraging the transfer of technologies and business processes, to improve productivity (output per worker). Encouraging globalized free trade via containerization is a major recent example.
- Tax reduction, to provide incentives to work, invest and take risks. Lowering income tax rates and eliminating or lowering tariffs are examples of such policies.
- Investments in new capital equipment and research and development (R&D), to further improve productivity. Allowing businesses to depreciate capital equipment more rapidly (e.g., over one year as opposed to 10) gives them an immediate financial incentive to invest in such equipment.
- Reduction in government regulations, to encourage business formation and expansion.
A basis of supply-side economics is the Laffer curve, a theoretical relationship between rates of taxation and government revenue. The Laffer curve suggests that when the tax level is too high, lowering tax rates will boost government revenue through higher economic growth, though the level at which rates are deemed "too high" is disputed. Critics also argue that several large tax cuts in the United States over the last 40 years have not increased revenue. (Full article...) - Image 13
Jan Tinbergen (/ˈtɪnbɜːrɡən/ TIN-bur-gən,Dutch: [jɑn ˈtɪmbɛrɣə(n)]; 12 April 1903 – 9 June 1994) was a Dutch economist who was awarded the first Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1969, which he shared with Ragnar Frisch for having developed and applied dynamic models for the analysis of economic processes. He is widely considered to be one of the most influential economists of the 20th century and one of the founding fathers of econometrics.
His important contributions to econometrics include the development of the first macroeconometric models, the solution of the identification problem, and the understanding of dynamic models. Tinbergen was a founding trustee of Economists for Peace and Security. In 1945, he founded the Bureau for Economic Policy Analysis (CPB) and was the agency's first director. (Full article...) - Image 14
Simon Smith Kuznets (/ˈkʌznɛts/ KUZ-nets;‹The template Lang-rus is being considered for deletion.› Russian: Семён Абра́мович Кузне́ц,IPA: [sʲɪˈmʲɵn ɐˈbraməvʲɪtɕ kʊzʲˈnʲets]; April 30, 1901 – July 8, 1985) was a Russian-born American economist and statistician who received the 1971 Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences "for his empirically founded interpretation of economic growth which has led to new and deepened insight into the economic and social structure and process of development."
Kuznets made a decisive contribution to the transformation of economics into an empirical science and to the formation of quantitative economic history. Kuznets pioneered the concept of gross domestic product, which seeks to capture all economic production in a state by a single measure. (Full article...) - Image 15
James McGill Buchanan Jr. (/bjuːˈkænən/ bew-KAN-ən; October 3, 1919 – January 9, 2013) was an American economist known for his work on public choice theory originally outlined in his most famous work, The Calculus of Consent, co-authored with Gordon Tullock in 1962. He continued to develop the theory, eventually receiving the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1986. Buchanan's work initiated research on how politicians' and bureaucrats' self-interest, utility maximization, and other non-wealth-maximizing considerations affect their decision-making. He was a member of the Board of Advisors of The Independent Institute as well as of the Institute of Economic Affairs, a member of the Mont Pelerin Society (MPS) and MPS president from 1984 to 1986, a Distinguished Senior Fellow of the Cato Institute, and professor at George Mason University. (Full article...) - Image 16
Joseph Alois Schumpeter (German: [ˈʃʊmpeːtɐ]; February 8, 1883 – January 8, 1950) was an Austrian political economist. He served briefly as Finance Minister of Austria in 1919. In 1932, he emigrated to the United States to become a professor at Harvard University, where he remained until the end of his career, and in 1939 obtained American citizenship.
Schumpeter was one of the most influential economists of the early 20th century, and popularized creative destruction, a term coined by Werner Sombart. His magnum opus is considered Capitalism, Socialism and Democracy. (Full article...) - Image 17The pluralism in economics movement is a campaign to change the teaching and research in economics towards more openness in its approaches, topics and standpoints it considers. The goal of the movement is to "reinvigorate the discipline ... [and bring] economics back into the service of society". Some have argued that economics had greater scientific pluralism in the past compared to the monist approach that is prevalent today. Pluralism encourages the inclusion of a wide variety of neoclassical and heterodox economic theories—including classical, Post-Keynesian, institutional, ecological, evolutionary, feminist, Marxist, and Austrian economics, stating that "each tradition of thought adds something unique and valuable to economic scholarship". (Full article...)
- Image 18
Johann Heinrich von Thünen (24 June 1783 – 22 September 1850), sometimes spelled Thuenen, was a prominent nineteenth-century economist and a native of Mecklenburg-Strelitz, now in northern Germany.
Even though he never held a professorial position, Thünen had substantial influence on economics. He has been described as one of the founders of agricultural economics and economic geography. He made substantial contributions to economic debates on rent, land use, and wages. (Full article...) - Image 19Neo-Marxism is a collection of Marxist schools of thought originating from 20th-century approaches to amend or extend Marxism and Marxist theory, typically by incorporating elements from other intellectual traditions such as critical theory, psychoanalysis, or existentialism. Neo-Marxism comes under the broader framework of the New Left. In a sociological sense, neo-Marxism adds Max Weber's broader understanding of social inequality, such as status and power, to Marxist philosophy.
As with many uses of the prefix neo-, some theorists and groups who are designated as neo-Marxists have attempted to supplement the perceived deficiencies of orthodox Marxism or dialectical materialism. Many prominent neo-Marxists, such as Herbert Marcuse and other members of the Frankfurt School, have historically been sociologists and psychologists. (Full article...) - Image 20
Karl Marx (German: [ˈkaʁl ˈmaʁks]; 5 May 1818 – 14 March 1883) was a German philosopher, political theorist, economist, journalist, and revolutionary socialist. He is best-known for the 1848 pamphlet The Communist Manifesto (written with Friedrich Engels), and his three-volume Das Kapital (1867–1894), a critique of classical political economy which employs his theory of historical materialism in an analysis of capitalism, in the culmination of his life's work. Marx's ideas and their subsequent development, collectively known as Marxism, have had enormous influence.
Born in Trier in the Kingdom of Prussia, Marx studied at the universities of Bonn and Berlin, and received a doctorate in philosophy from the University of Jena in 1841. A Young Hegelian, he was influenced by the philosophy of Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, and both critiqued and developed Hegel's ideas in works such as The German Ideology (written 1846) and the Grundrisse (written 1857–1858). While in Paris, Marx wrote his Economic and Philosophic Manuscripts of 1844 and met Engels, who became his closest friend and collaborator. After moving to Brussels in 1845, they were active in the Communist League, and in 1848 they wrote The Communist Manifesto, which expresses Marx's ideas and lays out a programme for revolution. Marx was expelled from Belgium and Germany, and in 1849 moved to London, where he wrote The Eighteenth Brumaire of Louis Bonaparte (1852) and Das Kapital. From 1864, Marx was involved in the International Workingmen's Association (First International), in which he fought the influence of anarchists led by Mikhail Bakunin. In his Critique of the Gotha Programme (1875), Marx wrote on revolution, the state and the transition to communism. He died stateless in 1883 and was buried in Highgate Cemetery. (Full article...) - Image 21Keynesian economics (/ˈkeɪnziən/ KAYN-zee-ən; sometimes Keynesianism, named after British economist John Maynard Keynes) are the various macroeconomic theories and models of how aggregate demand (total spending in the economy) strongly influences economic output and inflation. In the Keynesian view, aggregate demand does not necessarily equal the productive capacity of the economy. It is influenced by a host of factors that sometimes behave erratically and impact production, employment, and inflation.
Keynesian economists generally argue that aggregate demand is volatile and unstable and that, consequently, a market economy often experiences inefficient macroeconomic outcomes, including recessions when demand is too low and inflation when demand is too high. Further, they argue that these economic fluctuations can be mitigated by economic policy responses coordinated between a government and their central bank. In particular, fiscal policy actions taken by the government and monetary policy actions taken by the central bank, can help stabilize economic output, inflation, and unemployment over the business cycle. Keynesian economists generally advocate a regulated market economy – predominantly private sector, but with an active role for government intervention during recessions and depressions. (Full article...) - Image 22

Slogan in Bhutan about gross national happiness in Thimphu's School of Traditional Arts.
Buddhist economics is a spiritual and philosophical approach to the study of economics. It examines the psychology of the human mind and the emotions that direct economic activity, in particular concepts such as anxiety, aspirations and self-actualization principles. In the view of its proponents, Buddhist economics aims to clear the confusion about what is harmful and what is beneficial in the range of human activities involving the production and consumption of goods and services, ultimately trying to make human beings ethically mature. The ideology's stated purpose is to "find a middle way between a purely mundane society and an immobile, conventional society."
The most fundamental feature of Buddhist economics is seeing "people interdependent with one another and with Nature." (Full article...) - Image 23

Antoine Augustin Cournot (French: [ɑ̃twan oɡystɛ̃ kuʁno]; 28 August 1801 – 31 March 1877) was a French philosopher and mathematician who contributed to the development of economics. (Full article...) - Image 24

The mythological Judgement of Paris required selecting from three incomparable alternatives (the goddesses shown).
Decision theory or the theory of rational choice is a branch of probability, economics, and analytic philosophy that uses expected utility and probability to model how individuals would behave rationally under uncertainty. It differs from the cognitive and behavioral sciences in that it is mainly prescriptive and concerned with identifying optimal decisions for a rational agent, rather than describing how people actually make decisions. Despite this, the field is important to the study of real human behavior by social scientists, as it lays the foundations to mathematically model and analyze individuals in fields such as sociology, economics, criminology, cognitive science, moral philosophy and political science. (Full article...) - Image 25
Marie-Esprit-Léon Walras (French: [valʁas]; 16 December 1834 – 5 January 1910) was a French mathematical economist and Georgist. He formulated the marginal theory of value (independently of William Stanley Jevons and Carl Menger) and pioneered the development of general equilibrium theory. Walras is best known for his book Éléments d'économie politique pure, a work that has contributed greatly to the mathematization of economics through the concept of general equilibrium. The definition of the role of the entrepreneur found in it was also taken up and amplified by Joseph Schumpeter.
For Walras, exchanges only take place after a Walrasian tâtonnement (French for "trial and error"), guided by the auctioneer, has made it possible to reach market equilibrium. It was the general equilibrium obtained from a single hypothesis, rarity, that led Joseph Schumpeter to consider him "the greatest of all economists". The notion of general equilibrium was very quickly adopted by major economists such as Vilfredo Pareto, Knut Wicksell and Gustav Cassel. John Hicks and Paul Samuelson used the Walrasian contribution in the elaboration of the neoclassical synthesis. For their part, Kenneth Arrow and Gérard Debreu, from the perspective of a logician and a mathematician, determined the conditions necessary for equilibrium. (Full article...)
Did you know...
- ... that Elizabeth Wilkins chose to work at the Federal Trade Commission on the hope that the agency is now positioned to address economic injustice?
- ... that environmental economist V. Kerry Smith has been described as a "Renaissance Man of Economics"?
- ... that a banker was named the prime minister of Equatorial Guinea after his predecessor resigned during an economic crisis?
- ... that scientists from the Institutum Divi Thomae raised silkworms at Saint Gregory Seminary during World War II as a form of economic warfare against Japan?
- ... that the selection of Palu as capital of Palu Regency led to protests from the nearby town of Donggala, concerned they would lose out on economic development?
- ... that soprano Galina Pisarenko studied economics, English, and Norwegian at the same time she was studying to become a professional opera singer?
Need help?
Do you have a question about Economics that you can't find the answer to?
Consider asking it at the Wikipedia reference desk.
Get involved
For editor resources and to collaborate with other editors on improving Wikipedia's Economics-related articles, see WikiProject Economics.
Selected images
- Image 1São Paulo Stock Exchange in Brazil, an electronic trading network that brings together buyers and sellers through an electronic trading platform
- Image 5Pollution can be a simple example of market failure; if costs of production are not borne by producers but are by the environment, accident victims or others, then prices are distorted.
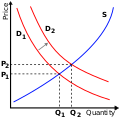
- Image 6The supply and demand model describes how prices vary as a result of a balance between product availability and demand. The graph depicts an increase in demand from D1 to D2 and the resulting increase in price and quantity required to reach a new equilibrium point on the supply curve (S).
- Image 8The publication of Adam Smith's The Wealth of Nations in 1776 is considered to be the first formalisation of economic thought.
- Image 9The Marxist critique of political economy comes from the work of German philosopher Karl Marx.
- Image 10A 1638 painting of a French seaport during the heyday of mercantilism
- Image 11Economists study trade, production, and consumption decisions, including those that occur in a traditional marketplace
- Image 12An environmental scientist sampling water
In the news
- 25 April 2025 – German economic crisis
- The German government cuts its economic growth forecast to zero, with the Deutsche Bundesbank estimating a future recession. Minister of Economic Affairs Robert Habeck accuses U.S. President Donald Trump's Liberation Day tariffs of being the primary reason for Germany's continued economic crisis. (DW)
- 11 April 2025 – Tariffs in the second Trump administration
- China states that it will not respond to any further U.S. tariff increases, as U.S. goods have already been priced out of the Chinese market by existing tariffs, but may still impose other economic measures. (CNBC)
- 7 April 2025 – Tariffs in the second Trump administration, Executive orders in the second presidency of Donald Trump
- European Commission president Ursula von der Leyen offers to negotiate with Trump to avoid a trade war and further economic panic, including a zero-for-zero tariff deal on all industrial goods. (Politico) (Euronews)
Subcategories
Subtopics
Associated Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
- Commons
Free media repository - Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals - Wikidata
Free knowledge base - Wikinews
Free-content news - Wikiquote
Collection of quotations - Wikisource
Free-content library - Wikiversity
Free learning tools - Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus