Portal:Tropical cyclones
The Tropical Cyclones Portal

A tropical cyclone is a storm system characterized by a large low-pressure center, a closed low-level circulation and a spiral arrangement of numerous thunderstorms that produce strong winds and heavy rainfall. Tropical cyclones feed on the heat released when moist air rises, resulting in condensation of water vapor contained in the moist air. They are fueled by a different heat mechanism than other cyclonic windstorms such as Nor'easters, European windstorms and polar lows, leading to their classification as "warm core" storm systems. Most tropical cyclones originate in the doldrums, approximately ten degrees from the Equator.
The term "tropical" refers to both the geographic origin of these systems, which form almost exclusively in tropical regions of the globe, as well as to their formation in maritime tropical air masses. The term "cyclone" refers to such storms' cyclonic nature, with anticlockwise rotation in the Northern Hemisphere and clockwise rotation in the Southern Hemisphere. Depending on its location and intensity, a tropical cyclone may be referred to by names such as "hurricane", "typhoon", "tropical storm", "cyclonic storm", "tropical depression" or simply "cyclone".
Types of cyclone: 1. A "Typhoon" is a tropical cyclone located in the North-west Pacific Ocean which has the most cyclonic activity and storms occur year-round. 2. A "Hurricane" is also a tropical cyclone located at the North Atlantic Ocean or North-east Pacific Ocean which have an average storm activity and storms typically form between May 15 and November 30. 3. A "Cyclone" is a tropical cyclone that occurs in the South Pacific and Indian Oceans.
Selected named cyclone -
Cyclonic Storm Komen (/ˈkoʊ.mɛn/) was an unusual tropical cyclone that originated near the southern coast of Bangladesh and later struck the same country while drifting over the northern Bay of Bengal. The second named storm of the 2015 season, Komen brought several days of heavy rainfall to Myanmar, Bangladesh, and India. It formed as a depression on July 26 over the Ganges delta and moved in a circular motion around the northern Bay of Bengal. Komen intensified into a 75 km/h (45 mph) cyclonic storm and moved ashore southeastern Bangladesh on July 30. The system turned westward over land and was last noted over eastern India on August 2.
Across its path, Komen dropped torrential rainfall, primarily in northwestern Myanmar where the precipitation totaled at 840 mm (33 in) in Paletwa. The rains compounded upon ongoing flooding and contributed to the worst flooding in the country in a century. About 1.7 million people were forced to evacuate as flood waters inundated houses to their rooftops. About 510,000 houses in the country were damaged or destroyed, and many residents lost their source of income as 667,221 acres (270,015 hectares) of crop fields were damaged. The floods killed 132 people, of which at least 39 were directly related to Komen. The government requested assistance from the international community to cope with the disaster, considered the worst in the country since Cyclone Nargis in 2008. Elsewhere, the storm's flooding damaged 88,900 houses in Bangladesh and covered crop fields for a week; Komen killed 45 people in the country, some of whom due to illnesses spread by the storm. Later, floodwaters affected southeastern India, killing 103 people and damaging or destroying 476,046 houses. (Full article...)
Selected article -
The effects of Hurricane Isabel in Virginia proved to be the costliest disaster in the history of Virginia. Hurricane Isabel formed from a tropical wave on September 6, 2003, in the tropical Atlantic Ocean. It moved northwestward, and within an environment of light wind shear and warm waters it steadily strengthened to reach peak winds of 265 km/h (165 mph) on September 11. After fluctuating in intensity for four days, Isabel gradually weakened and made landfall on the Outer Banks of North Carolina with winds of 165 km/h (103 mph) on September 18. It quickly weakened over land as it passed through central Virginia, and Isabel became extratropical over western Pennsylvania on September 19.
Strong winds from the hurricane affected 99 counties and cities in the state, which downed thousands of trees and left about 1.8 million without power. The storm surge impacted much of the southeastern portion of the state, peaking at around 9 feet (2.7 m) in Richmond along the James River; the surge caused significant damage to homes along riverways. The nationwide maximum rainfall total from the hurricane was 20.2 inches (510 mm) in Sherando, Virginia. In the state's mountainous region, heavy rainfall caused severe and damaging flash flooding. The hurricane caused about $1.85 billion (2003 USD, $2.17 billion 2008 USD) in damage and 36 deaths in the state—10 directly from the storm's effects and 22 indirectly related. (Full article...)
Selected image -

Selected season -

The 1999–2000 South-West Indian Ocean tropical cyclone season was the first on record in which two storms – Leon–Eline and Hudah – struck Mozambique at tropical cyclone intensity, or with maximum sustained winds of at least 120 km/h (75 mph). The most notable storm of the season was Eline, which was the third longest-lasting storm on record in the basin. It lasted for 29 days while traversing the southern Indian Ocean, making the strongest landfall in decades along eastern Madagascar in late February. The storm was the first in a series of three storms that struck the country in early 2000, along with Gloria in March and Hudah in April. Collectively, the three storms killed at least 316 people. The season started on November 1, 1999, and ended for most of the basin on April 30, 2000; for Mauritius and the Seychelles, the season continued until May 15. These dates conventionally delimit the period of each year when most tropical cyclones form in the basin.
Despite the destructive nature of the season, it began later than usual. Cyclone Astride originated toward the end of December, bringing rainfall and gusty winds to northern Madagascar while in the region. In January, Cyclones Babiola and Connie both formed east of Madagascar and took southerly tracks. Connie passed near Réunion island, producing 1,752 mm (69.0 in) of rainfall in the mountainous peaks and killing two people. Eline, the longest lasting storm of the season, struck Mozambique while the country was experiencing its worst flooding in 50 years, collectively causing around 700 deaths and about $500 million in damage. The storm also killed 12 people in Zimbabwe and 21 in South Africa. Just two weeks after Eline struck Madagascar, Tropical Storm Gloria affected the same general region, bringing additional deaths and damage. Cyclone Hudah in April was the strongest storm of the season, reaching peak 10‑minute winds of 220 km/h (140 mph). It caused three deaths in Mozambique, although its effects were worse in Madagascar, where there were 111 deaths. The final storm of the season was Tropical Storm Innocente, which dissipated on April 24. In addition to the named storms, there were four unnamed tropical disturbances or storms, as well as one subtropical cyclone that formed in the southern Mozambique Channel.
(Full article...)Related portals
Currently active tropical cyclones
Italicized basins are unofficial.
- North Atlantic (2025)
- No active systems
- East and Central Pacific (2025)
- No active systems
- West Pacific (2025)
- No active systems
- North Indian Ocean (2025)
- No active systems
- Mediterranean (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South-West Indian Ocean (2024–25)
- No active systems
- Australian region (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Pacific (2024–25)
- No active systems
- South Atlantic (2024–25)
- No active systems
Last updated: 11:23, 23 April 2025 (UTC)
Tropical cyclone anniversaries

May 2
- 1994 - A powerful cyclone made landfall near the Burma–Bangladeshi border. The cyclone caused 285 deaths and over $125 million of damage.
- 2008 - Cyclone Nargis (pictured) struck the Ayeyarwady Region of Burma near Yangon, inflicting catastrophic destruction and causing 138,373 fatalities; it was the fifth-deadliest tropical cyclone on record.

May 3
- 2019 - Cyclone Fani (pictured) struck eastern India. It killed 89 people and left US$8.9 billion in damage.
- 2024 - Tropical Storm Hidaya struck eastern Tanzania, one of only three storms on record to strike the country. Hidaya killed five people and damaged more than 1,500 houses.

May 4
- 1982 - A tropical cyclone struck southern Burma, where it killed five people.
- 2009 - Typhoon Kujira (pictured) reaches peak strength as a Category 4 typhoon, after killing 28 people and causing P1.25 million (US$27 million) in damage in the Philippines.
Did you know…


- …that the Joint Typhoon Warning Center considers that Typhoon Vera (pictured) of 1986 is actually two distinct systems, formed from two separated low-level circulations?
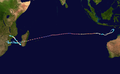
- …that Cyclone Freddy (track pictured) in 2023 was the longest-lasting tropical cyclone recorded?
- …that the typhoons of 2024—Yinxing, Toraji, Usagi, and Man-yi (pictured)—made history as the first recorded instance since 1951 of four tropical cyclones coexisting in November?
- …that Hurricane Otis (pictured) in 2023 was the first Pacific hurricane to make landfall at Category 5 intensity and surpassed Hurricane Patricia as the strongest landfalling Pacific hurricane on record?
General images -

The 2012 Pacific hurricane season was an above-average year in which seventeen named storms formed. The hurricane season officially began on May 15 in the east Pacific—defined as the region east of 140°W—and on June 1 in the central Pacific—defined as the region west of 140°W to the International Date Line—and ended on November 30 in both regions. These dates conventionally delimit the period during each year when most tropical cyclones form in the northeastern Pacific Ocean. This year, the first storm of the season, Tropical Storm Aletta, formed on May 14, and the last, Tropical Storm Rosa, dissipated on November 3.
The season produced seventeen tropical storms; ten became hurricanes, and five further intensified into major hurricanes. Impact during the season was relatively minimal. In late May, Hurricane Bud paralleled the western Mexico coastline before dissipating, causing minor damage and but no reported fatalities. In mid-June, Hurricane Carlotta came ashore in Oaxaca at Category 2 hurricane intensity, making it the easternmost tropical cyclone in the basin to make landfall at hurricane intensity since 1966. The storm killed seven and caused $12.4 million (2012 USD) in damage. (Full article...)
Topics
Subcategories
Related WikiProjects
WikiProject Tropical cyclones is the central point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of tropical cyclones. Feel free to help!
WikiProject Weather is the main center point of coordination for Wikipedia's coverage of meteorology in general, and the parent project of WikiProject Tropical cyclones. Three other branches of WikiProject Weather in particular share significant overlaps with WikiProject Tropical cyclones:
- The Non-tropical storms task force coordinates most of Wikipedia's coverage on extratropical cyclones, which tropical cyclones often transition into near the end of their lifespan.
- The Floods task force takes on the scope of flooding events all over the world, with rainfall from tropical cyclones a significant factor in many of them.
- WikiProject Severe weather documents the effects of extreme weather such as tornadoes, which landfalling tropical cyclones can produce.
Things you can do
 | Here are some tasks awaiting attention:
|
Wikimedia
The following Wikimedia Foundation sister projects provide more on this subject:
- Commons
Free media repository - Wikibooks
Free textbooks and manuals - Wikidata
Free knowledge base - Wikinews
Free-content news - Wikiquote
Collection of quotations - Wikisource
Free-content library - Wikiversity
Free learning tools - Wikivoyage
Free travel guide - Wiktionary
Dictionary and thesaurus















































