Max Carl Wilhelm Weber
Max Carl Wilhelm Weber van Bosse or Max Wilhelm Carl Weber (5 December 1852 – 7 February 1937) was a German-Dutch zoologist and biogeographer.
Weber studied at the University of Bonn, then at the Humboldt University in Berlin with the zoologist Eduard Carl von Martens (1831–1904). He obtained his doctorate in 1877. Weber taught at the University of Utrecht then participated in an expedition to the Barents Sea. He became Professor of Zoology, Anatomy and Physiology at the University of Amsterdam in 1883. In the same year he received naturalised Dutch citizenship.
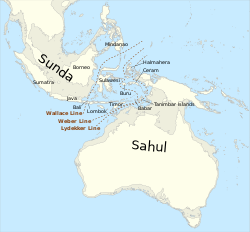
His discoveries as leader of the Siboga Expedition led him to conclude that Wallace's Line was placed too far to the west. His studies, along with others, led to a series of alternative lines to be proposed to delimit two major biogeographic realms, the Australasian realm and the Indomalayan realm. These lines were based on the fauna and flora in general, including the mammalian fauna. Later, Pelseneer published an influential paper on this topic, in which he proposed to call his preferred limit Weber's Line, to honour Weber's contributions in that field. As is the case with plant species, faunal surveys revealed that for mollusks and most vertebrate groups Wallace’s line was not the most significant biogeographic boundary. The Tanimbar Island group, and not the boundary between Bali and Lombok, appears to be the major interface between the Oriental and Australasian regions for mammals and other terrestrial vertebrate groups.
With G.A.F. Molengraaff, Weber gave names to the Sahul Shelf and the Sunda Shelf in 1919.
Weber became member of the Royal Netherlands Academy of Arts and Sciences in 1887.
Weber is commemorated in the scientific names of three species of reptiles: Anomochilus weberi, Hydrosaurus weberi, and Pachydactylus weberi. Two species of mammal are also named after him: Prosciurillus weberi and Myotis weberi.
Publications
- Weber, M. [W. C.] (ed.), 1890-1907. Zoologische Ergebnisse einer Reise in Niederländisch Ost-Indien, 1 (1890-1891): [i-v], i-xi, maps I-III, 1-460, pls. I-XXV; 2 (1892): [i-v], 1-571, pls. I-XXX; 3 (1894): [i-v], 1-476, pls. I-XXII; 4 (1897-1907): [i-v], 1-453, pls. I-XVI (E. J. Brill, Leiden)OCLC 60765525.
- Weber, M. [W. C.], 1902. Introduction et description de l'expedition", I. Siboga-expeditieOCLC 647132542.
- Weber, M. [W. C.], 1904b. Enkele resultaten der Siboga-expeditie. Versl. gewone Vergad. wis- en natuurk. Afd. K. Akad. Wet. Amsterdam, 12 (2): 910-914.
- Weber, M. [W. C.] & L. F. de Beaufort, 1911-1962. The fishes of the Indo-Australian Archipelago, I (1911). Index of the ichthyological papers of P. Bleeker: i-xi, 1-410, 1 portrait; II. (1913). Malacopterygii, Myctophoidea, Ostariophysi: I Siluroidea: i-xx, 1-404, 1 portrait; III. (1916) Ostariophysi: II Cyprinoidea, Apodes, Synbranchii]: i-xv, 1-455; IV. (1922) Heteromi, Solenichthyes, Synentognathi, Percesoces, Labyrinthici, Microcyprini]: i-xiii, 1-410OCLC 646844856
Gallery
- Portrait of Max Wilhelm Carl
- Max Wilhelm Carl Weber and Anna Weber-van Bosse around 1890
- Siboga expedition group portrait in laboratory
- Siboga expedition group portrait
Taxon described by him
Taxon named in his honor
- The pipefish Cosmocampus maxweberi (Whitley, 1933) was named after him.
Abyssal plain named in his honor
Weber Deep with a depth of 7,351 meters, (24,117 feet, 4.56 miles) in the Banda Sea.
See also
References
Citations
- Querner, H., 1976. Weber, Max Wilhelm Carl. In : C. C. Gillispie (ed.), Dictionary of scientific biography, 14 : 203 (Charles Scribner's Sons, New York).
- Pieters, Florence F. J. M. et Jaap de Visser, 1993. The scientific career of the zoologist Max Wilhelm Carl Weber (1852-1937). Bijdragen tot de Dierkunde, 62 (4): 193-214.



